Effectiveness of combination therapy with nifedipine GITS: a prospective, 12-week observational study (AdADOSE)
- PMID: 25956918
- PMCID: PMC4448540
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-015-0037-x
Effectiveness of combination therapy with nifedipine GITS: a prospective, 12-week observational study (AdADOSE)
Abstract
Background: Observational studies can provide important information on the efficacy and safety of antihypertensive agents in the real-life clinical setting. AdADOSE was a large observational study to assess the effectiveness of nifedipine GITS in combination with other antihypertensive agent(s). The study was also the first to examine the role of combination therapy with nifedipine GITS in the Middle East, Pakistan and Russia, regions that are associated with particularly high cardiovascular risk.
Methods: AdADOSE was a 12-week, international, multicenter, prospective, observational study. Patients with hypertension (ie, blood pressure [BP] >140/90 mm Hg, or >130/80 mm Hg in patients at high or very high cardiovascular risk) received once-daily nifedipine GITS (30, 60 or 90 mg) in combination with another antihypertensive or as add-on to existing therapy. The primary study endpoint was the proportion of patients who achieved the target BP of <140/90 mm Hg (or <130/80 mm Hg for those at high or very high cardiovascular risk). Study outcomes are reported by descriptive statistics.
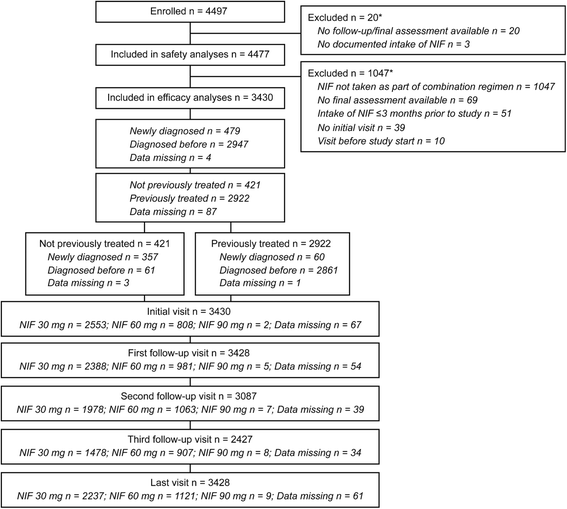
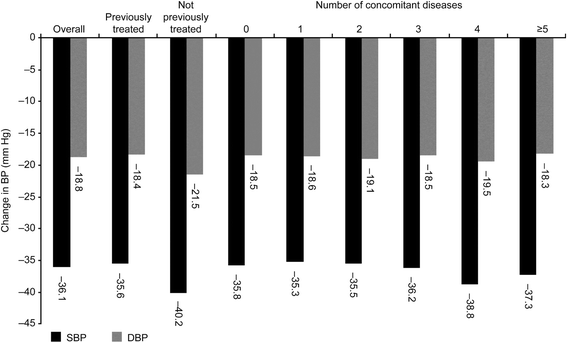
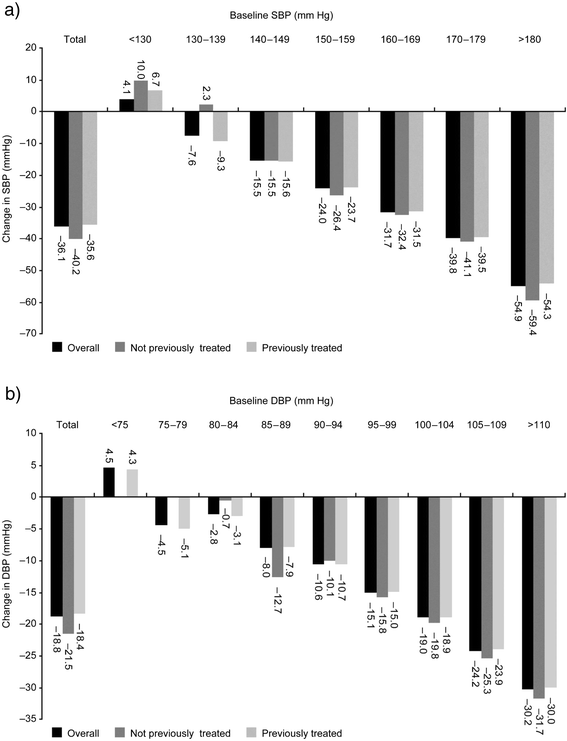
Results: The study enrolled 4497 patients (n = 4477, safety population; n = 3430, efficacy population). Baseline mean systolic/diastolic BP (SBP/DBP) was 166.4/99.7 mm Hg; 85.2 % of patients had received prior antihypertensive treatment, and 90.6 % had ≥ 1 concomitant diseases. Following combination treatment with nifedipine GITS, target BP was achieved by 64.8% of patients without concomitant diseases, and by 56.5%, 32.3% and 22.6% with 1, 2-3 and >3 concomitant diseases, respectively. The proportion of patients achieving target BP was 51.5% in previously untreated and 33.7% in previously treated patients. Nifedipine GITS combination treatment provided mean SBP/DBP changes of -36.1/-18.8 mm Hg in all patients, -40.2/-21.5 mm Hg in previously untreated patients, and -35.6/-18.4 mm Hg in previously treated patients, with similar BP reductions irrespective of the number of concomitant diseases. Drug-related adverse events (AEs) were reported in 2.6% patients. There were no serious AEs and only 0.8% of patients discontinued due to drug-related AEs.
Conclusions: Combination therapy with nifedipine GITS in a real-life observational setting was highly effective in reducing SBP/DBP in a range of hypertensive patients, with low rates of treatment-related AEs.
Trial registration: at ClinicalTrials.gov registration number NCT01118286 .
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination therapy with nifedipine GITS 60 mg: subanalysis of a prospective, 12-week observational study (AdADOSE).Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016;38(1):71-80. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2015.1060986. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26331311 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of long-acting nifedipine GITS/OROS monotherapy or combination therapy in hypertensive patients: results of a 12-week international, prospective, multicentre, observational study.Clin Drug Investig. 2011;31(9):631-42. doi: 10.2165/11588970-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2011. PMID: 21591818
-
A study of losartan, alone or with hydrochlorothiazide vs nifedipine GITS in elderly patients with diastolic hypertension.J Hum Hypertens. 1998 Oct;12(10):693-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.jhh.1000687. J Hum Hypertens. 1998. PMID: 9819017 Clinical Trial.
-
Current treatment of patients with hypertension: therapeutic implications of INSIGHT.Drugs. 2003;63(14):1435-44. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363140-00001. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12834362 Review.
-
[Atenolol/nifedipine combination: efficacy and tolerability of low dose synergistic bitherapy in the treatment of arterial hypertension].Drugs. 1998;56 Suppl 2:31-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199856002-00004. Drugs. 1998. PMID: 9813740 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Clinical efficacy of various anti-hypertensive regimens in hypertensive women of Punjab; a longitudinal cohort study.BMC Womens Health. 2020 Aug 1;20(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12905-020-01033-2. BMC Womens Health. 2020. PMID: 32738879 Free PMC article.
-
Combination therapy with nifedipine GITS 60 mg: subanalysis of a prospective, 12-week observational study (AdADOSE).Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016;38(1):71-80. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2015.1060986. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26331311 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of baseline blood pressure on the magnitude of blood pressure lowering by nifedipine gastrointestinal therapeutic system: refreshing the Wilder's principle.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Nov 6;11:3179-3186. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S143551. eCollection 2017. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017. PMID: 29158664 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Knowledge and Attitudes Towards Clinical Trial Participation in Oman: A cross-sectional study.Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2018 Feb;18(1):e54-e60. doi: 10.18295/squmj.2018.18.01.009. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J. 2018. PMID: 29666682 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and Tolerability of Nifedipine GITS in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Uncontrolled Hypertension: A Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study (ADRENAL).Adv Ther. 2021 Sep;38(9):4771-4785. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01850-3. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34331258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Heart Association . Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2004 Update. Dallas: American Heart Association; 2003.
-
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2002. Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life. World Health Organization. [http://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/whr02_en.pdf] - PubMed
-
- Poole-Wilson PA, Lubsen J, Kirwan BA, van Dalen FJ, Wagener G, Danchin N, et al. Effect of long-acting nifedipine on mortality and cardiovascular morbidity in patients with stable angina requiring treatment (ACTION trial): randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2004;364:849–57. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16980-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

