Is this the right normalization? A diagnostic tool for ChIP-seq normalization
- PMID: 25957089
- PMCID: PMC4448883
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-015-0579-z
Is this the right normalization? A diagnostic tool for ChIP-seq normalization
Abstract
Background: Chip-seq experiments are becoming a standard approach for genome-wide profiling protein-DNA interactions, such as detecting transcription factor binding sites, histone modification marks and RNA Polymerase II occupancy. However, when comparing a ChIP sample versus a control sample, such as Input DNA, normalization procedures have to be applied in order to remove experimental source of biases. Despite the substantial impact that the choice of the normalization method can have on the results of a ChIP-seq data analysis, their assessment is not fully explored in the literature. In particular, there are no diagnostic tools that show whether the applied normalization is indeed appropriate for the data being analyzed.
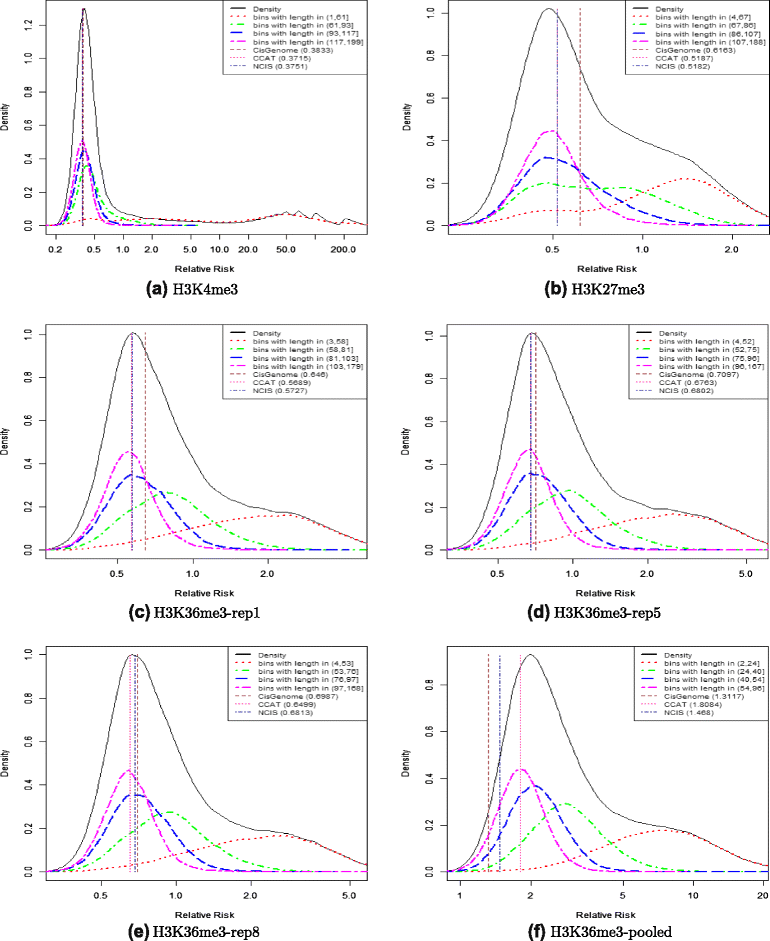
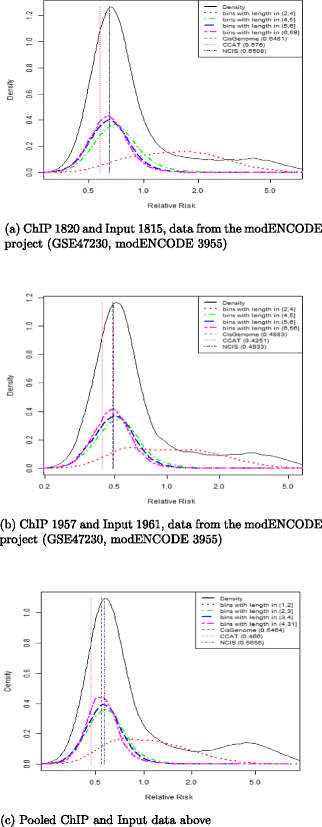
Results: In this work we propose a novel diagnostic tool to examine the appropriateness of the estimated normalization procedure. By plotting the empirical densities of log relative risks in bins of equal read count, along with the estimated normalization constant, after logarithmic transformation, the researcher is able to assess the appropriateness of the estimated normalization constant. We use the diagnostic plot to evaluate the appropriateness of the estimates obtained by CisGenome, NCIS and CCAT on several real data examples. Moreover, we show the impact that the choice of the normalization constant can have on standard tools for peak calling such as MACS or SICER. Finally, we propose a novel procedure for controlling the FDR using sample swapping. This procedure makes use of the estimated normalization constant in order to gain power over the naive choice of constant (used in MACS and SICER), which is the ratio of the total number of reads in the ChIP and Input samples.
Conclusions: Linear normalization approaches aim to estimate a scale factor, r, to adjust for different sequencing depths when comparing ChIP versus Input samples. The estimated scaling factor can easily be incorporated in many peak caller algorithms to improve the accuracy of the peak identification. The diagnostic plot proposed in this paper can be used to assess how adequate ChIP/Input normalization constants are, and thus it allows the user to choose the most adequate estimate for the analysis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Normalization of ChIP-seq data with control.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Aug 10;13:199. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-199. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22883957 Free PMC article.
-
Software for rapid time dependent ChIP-sequencing analysis (TDCA).BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Nov 25;18(1):521. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1936-x. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 29178831 Free PMC article.
-
ChIP-chip versus ChIP-seq: lessons for experimental design and data analysis.BMC Genomics. 2011 Feb 28;12:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-134. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21356108 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ChIP-seq in the discovery of transcription factor binding sites, differential gene regulation mechanism, epigenetic marks and beyond.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(18):2847-52. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.949201. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A short survey of computational analysis methods in analysing ChIP-seq data.Hum Genomics. 2011 Jan;5(2):117-23. doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-5-2-117. Hum Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21296745 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
metagene Profiles Analyses Reveal Regulatory Element's Factor-Specific Recruitment Patterns.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Aug 18;12(8):e1004751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004751. eCollection 2016 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27538250 Free PMC article.
-
The ENCODE Imputation Challenge: a critical assessment of methods for cross-cell type imputation of epigenomic profiles.Genome Biol. 2023 Apr 18;24(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02915-y. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37072822 Free PMC article.
-
NucTools: analysis of chromatin feature occupancy profiles from high-throughput sequencing data.BMC Genomics. 2017 Feb 14;18(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3580-2. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28196481 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of ChIP-seq data uncovers dynamic and sustained H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 modulation in cancer cells under hypoxia.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016 Nov 1;9:48. doi: 10.1186/s13072-016-0090-4. eCollection 2016. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2016. PMID: 27822313 Free PMC article.
-
T3E: a tool for characterising the epigenetic profile of transposable elements using ChIP-seq data.Mob DNA. 2022 Nov 30;13(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13100-022-00285-z. Mob DNA. 2022. PMID: 36451223 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

