Sodium channel Nav1.7 in vascular myocytes, endothelium, and innervating axons in human skin
- PMID: 25957174
- PMCID: PMC4447014
- DOI: 10.1186/s12990-015-0024-3
Sodium channel Nav1.7 in vascular myocytes, endothelium, and innervating axons in human skin
Abstract
Background: The skin is a morphologically complex organ that serves multiple complementary functions, including an important role in thermoregulation, which is mediated by a rich vasculature that is innervated by sympathetic and sensory endings. Two autosomal dominant disorders characterized by episodes of severe pain, inherited erythromelalgia (IEM) and paroxysmal extreme pain disorder (PEPD) have been directly linked to mutations that enhance the function of sodium channel Nav1.7. Pain attacks are accompanied by reddening of the skin in both disorders. Nav1.7 is known to be expressed at relatively high levels within both dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and sympathetic ganglion neurons, and mutations that enhance the activity of Nav1.7 have been shown to have profound effects on the excitability of both cell-types, suggesting that dysfunction of sympathetic and/or sensory fibers, which release vasoactive peptides at skin vasculature, may contribute to skin reddening in IEM and PEPD.
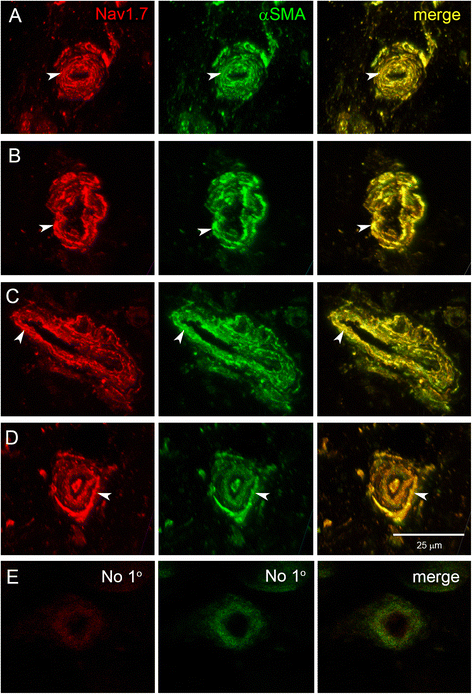
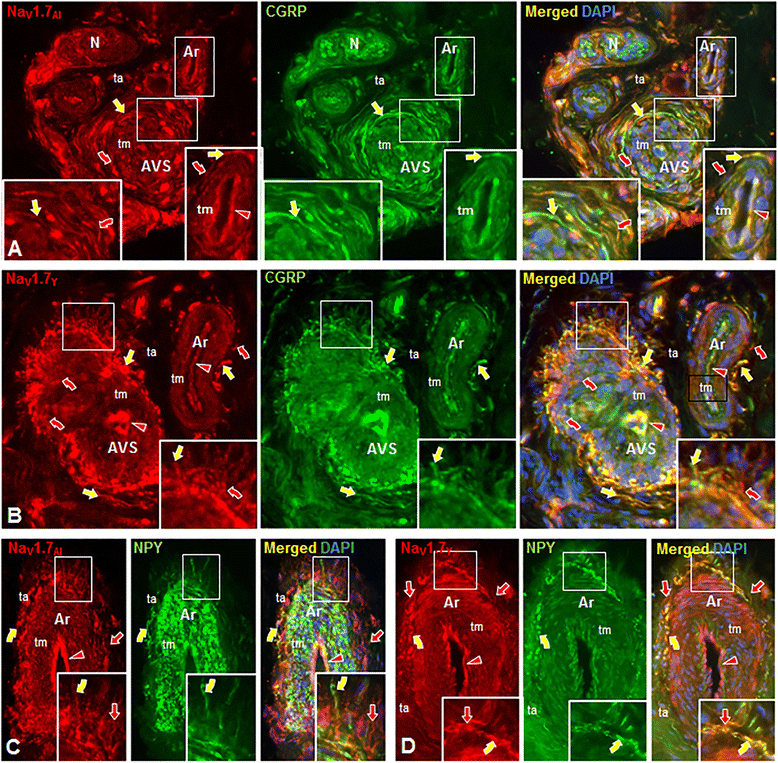
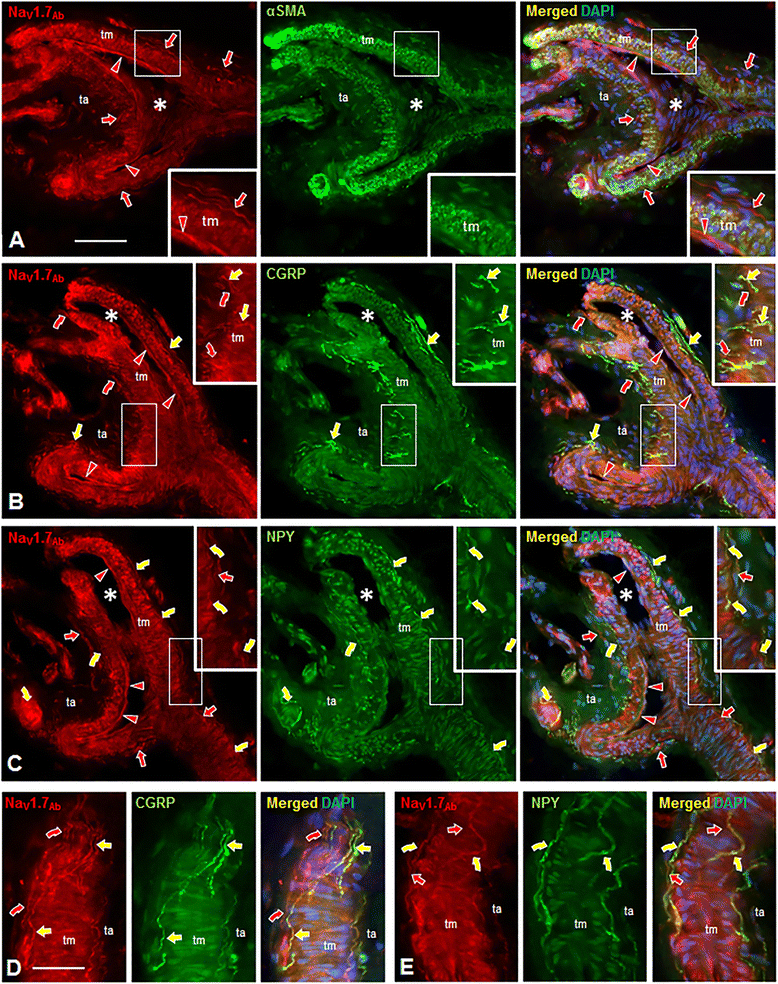
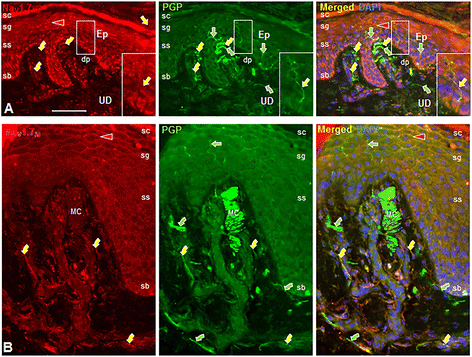
Results: In the present study, we demonstrate that smooth muscle cells of cutaneous arterioles and arteriole-venule shunts (AVS) in the skin express sodium channel Nav1.7. Moreover, Nav1.7 is expressed by endothelial cells lining the arterioles and AVS and by sensory and sympathetic fibers innervating these vascular elements.
Conclusions: These observations suggest that the activity of mutant Nav1.7 channels in smooth muscle cells of skin vasculature and innervating sensory and sympathetic fibers contribute to the skin reddening and/or pain in IEM and PEPD.
Figures

References
-
- Rice F, Albrecht P. Cutaneous Mechanisms of Tactile Perception: Morphological and Chemical Organization of the Innervation to the Skin. In: Basbaum A, Kaneko A, Shepard G, Westheimer G, editors. The Senses: A comprehensive Reference, vol 6, Somatosensation. San Diego: Academic Press; 2008. pp. 1–32.
-
- Albrecht PJ, Hou Q, Argoff CE, Storey JR, Wymer JP, Rice FL. Excessive peptidergic sensory innervation of cutaneous arteriole-venule shunts (AVS) in the palmar glabrous skin of fibromyalgia patients: implications for widespread deep tissue pain and fatigue. Pain Med. 2013;14(6):895–915. - PubMed
-
- Burton AC. The range and variability of the blood flow in the human fingers and the vasomotor regulation of body temperature. Am J Physiol. 1939;127:437–53.
-
- Johnson JM, Kellogg DL., Jr Thermoregulatory and thermal control in the human cutaneous circulation. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2010;2:825–53. - PubMed
-
- Kellogg DL., Jr In vivo mechanisms of cutaneous vasodilation and vasoconstriction in humans during thermoregulatory challenges. J Appl Physiol. 2006;100(5):1709–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

