Randomized controlled trial on drowning prevention for parents with children aged below five years in Bangladesh: a study protocol
- PMID: 25957574
- PMCID: PMC4434569
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-015-1823-1
Randomized controlled trial on drowning prevention for parents with children aged below five years in Bangladesh: a study protocol
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Randomized controlled trial on drowning prevention for parents with children aged below five years in Bangladesh: a study protocol.BMC Public Health. 2015 Sep 15;15:898. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-2169-4. BMC Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26374101 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Drowning is the third leading cause of death for children aged 0-4 years in many Asian countries, and is a serious but neglected health problem in low and middle-income countries like Bangladesh. The aim of the study is to outline the study protocol of a trial to test the efficacy of a mobile coach based intervention for the prevention of childhood drowning.
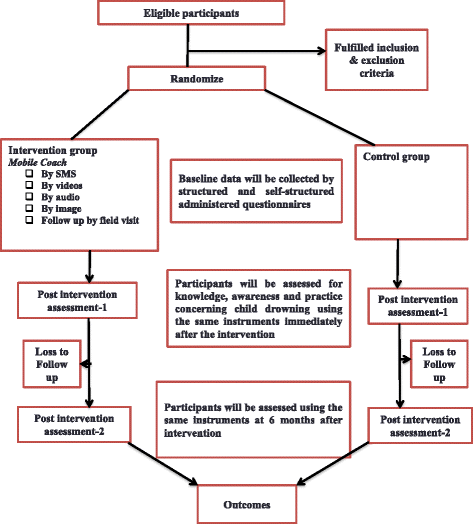
Method/design: A two-arm cluster randomized community trial will be conducted to test the efficacy of the mobile coach intervention for childhood drowning on parents with children below five years of age and compared to an assessment only control group. A total of 1680 parents in the villages with children aged below five years of age will participate. The village will be used as a randomized unit, randomly assigned to an intervention group (N = 840) receiving the mobile coach based intervention or an assessment only control group (N = 840). An individualized mobile coach intervention based on the demographic data and the individual will be developed, and SMSs, audio messages, videos and images about childhood drowning will be sent to the participants of the intervention group over a period of six months. The participants will receive per week one text message (SMS) and image and one video and audio text per month. The primary outcome measure will be increased knowledge and safety awareness, and behaviour practice about childhood drowning assessed at the six-month follow-up, and the secondary outcome measure will be the reduced incidence of childhood drowning in Bangladesh. The study assistants conducting the baseline and the follow-up assessments will be blinded regarding the group assignment.
Discussion: This is the first study testing a fully mobile coach intervention for childhood drowning prevention in Bangladesh. It is hoped that the programme will offer an effective and inexpensive way to prevent childhood drowning among children aged below five years and also increase the awareness of parents concerning the risks to their children from drowning.
Trial registration: ISRCTN13774693, 08/03/2015.
References
-
- WHO. Burden of disease: Deaths estimates for 2008 by cause for WHO member states, health statistics and health information systems- Disease and injury country estimates, 2012. Retrieved from http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/estimates_country/en/. index.html
-
- IDRC. International Drowning Research Centre, 2013. Dhaka, Bangladesh. http://swimsafe.org/wp-content/uploads/2009/08/Child-Drowningin-.
-
- Peden M, Oyegbite K, Ozanne-Smith J, Hyder AA, Branche C, Rahman F, et al. World report on child Injury prevention, summary. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical