Lymphoma and hypercalcemia in a pediatric orthotopic liver transplant patient
- PMID: 2595760
- PMCID: PMC2963945
- DOI: 10.1097/00007890-198912000-00022
Lymphoma and hypercalcemia in a pediatric orthotopic liver transplant patient
Abstract
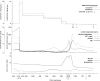
We present a case report of a pediatric orthotopic liver transplant recipient who developed lymphoma with hypercalcemia on cyclosporine and prednisone immunosuppression. This is the first reported posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder complicated by hypercalcemia, with a finding of an elevated 1,25 dihydroxyl vitamin D state, suggesting that it has a role in the pathophysiology of this B cell lymphoma hypercalcemia. The clinical course and management of this disorder with a 31-month follow-up are described.
Figures
References
-
- Bieber CP, Heberling RL, Jamieson SW, et al. Lymphoma in cardiac transplant recipients associated with cyclosporine A, prednisone and antithymocyte globulin (ATG). In: Purtilo DT, editor. Immune deficiency and cancer. Plenum; New York: 1984. p. 309.
-
- Schubach WH, Hackman R, Neiman PE, Miller G, Thomas ED. A monoclonal immunoblastic sarcoma in donor cells bearing Epstein-Barr virus genomes following allogeneic marrow grafting for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1982;60:180. - PubMed
-
- Canellos GP. Hypercalcemia in malignant lymphoma and leukemia. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1974;230:240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
