Widespread Proteome Remodeling and Aggregation in Aging C. elegans
- PMID: 25957690
- PMCID: PMC4643853
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.032
Widespread Proteome Remodeling and Aggregation in Aging C. elegans
Erratum in
-
Widespread Proteome Remodeling and Aggregation in Aging C. elegans.Cell. 2017 Feb 23;168(5):944. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.041. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28235202 No abstract available.
Abstract
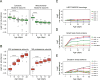
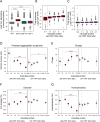
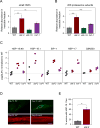
Aging has been associated with a progressive decline of proteostasis, but how this process affects proteome composition remains largely unexplored. Here, we profiled more than 5,000 proteins along the lifespan of the nematode C. elegans. We find that one-third of proteins change in abundance at least 2-fold during aging, resulting in a severe proteome imbalance. These changes are reduced in the long-lived daf-2 mutant but are enhanced in the short-lived daf-16 mutant. While ribosomal proteins decline and lose normal stoichiometry, proteasome complexes increase. Proteome imbalance is accompanied by widespread protein aggregation, with abundant proteins that exceed solubility contributing most to aggregate load. Notably, the properties by which proteins are selected for aggregation differ in the daf-2 mutant, and an increased formation of aggregates associated with small heat-shock proteins is observed. We suggest that sequestering proteins into chaperone-enriched aggregates is a protective strategy to slow proteostasis decline during nematode aging.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Arrasate M, Mitra S, Schweitzer ES, Segal MR, Finkbeiner S. Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature. 2004;431:805–810. - PubMed
-
- Balch WE, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–919. - PubMed
-
- Bensimon A, Heck AJ, Aebersold R. Mass spectrometry-based proteomics and network biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:379–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

