Integrating frequency and magnitude information in decision-making in schizophrenia: An account of patient performance on the Iowa Gambling Task
- PMID: 25959618
- PMCID: PMC4458199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.04.007
Integrating frequency and magnitude information in decision-making in schizophrenia: An account of patient performance on the Iowa Gambling Task
Abstract
Background: The Iowa Gambling Task (IGT; Bechara et al., 1994) has frequently been used to assess risky decision making in clinical populations, including patients with schizophrenia (SZ). Poor performance on the IGT is often attributed to reduced sensitivity to punishment, which contrasts with recent findings from reinforcement learning studies in schizophrenia.
Methods: In order to investigate possible sources of IGT performance deficits in SZ patients, we combined data from the IGT from 59 SZ patients and 43 demographically-matched controls with data from the Balloon Analog Risk Task (BART) in the same participants. Our analyses sought to specifically uncover the role of punishment sensitivity and delineate the capacity to integrate frequency and magnitude information in decision-making under risk.
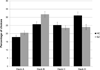
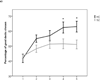
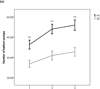
Results: Although SZ patients, on average, made more choices from disadvantageous decks than controls did on the IGT, they avoided decks with frequent punishments at a rate similar to controls. Patients also exhibited excessive loss-avoidance behavior on the BART.
Conclusions: We argue that, rather than stemming from reduced sensitivity to negative consequences, performance deficits on the IGT in SZ patients are more likely the result of a reinforcement learning deficit, specifically involving the integration of frequencies and magnitudes of rewards and punishments in the trial-by-trial estimation of expected value.
Keywords: Decision-making; Iowa Gambling Task (IGT); Reinforcement; Reward; Risk; Schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Andreasen NC. The Scale for the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS) Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa; 1984. - PubMed
-
- Bates AT, Liddle PF, Kiehl KA, Ngan ET. State dependent changes in error monitoring in schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res. 2004 May;38(3):347–356. - PubMed
-
- Bechara A, Damasio AR, Damasio H, Anderson SW. Insensitivity to future consequences following damage to human prefrontal cortex. Cognition. 1994 Jun;50(1–3):7–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

