The sex-specific association between BMI and coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 95 cohorts with 1·2 million participants
- PMID: 25960160
- PMCID: PMC4470268
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00086-8
The sex-specific association between BMI and coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 95 cohorts with 1·2 million participants
Abstract
Background: The risk of developing coronary heart disease differs by sex, and accumulating evidence suggests that sex differences exist in the effect of coronary risk factors on vascular risk. So far, the existence of a sex difference in the association between BMI and coronary heart disease has not been systematically studied. Since sexual dimorphisms in body composition exist, we postulated that the association between BMI and coronary heart disease would differ between women and men.
Methods: We did systematic searches of PubMed and Embase up to Feb 20, 2015, for studies of the longitudinal association between BMI and coronary heart disease in women and men from population-based cohorts. We excluded studies if they contained duplicate data from the same study, reported estimates only for Z scores or percentiles of BMI, did not report estimate uncertainty, did not report sex-specific estimates, recruited mainly individuals with a previous history of cardiovascular disease or from within selected populations, and those for which the full text was not available in English. We also included individual participant data from four large studies. Study results were pooled using random-effect models with inverse variance weighting. Our predefined primary endpoint was the pooled women-to-men ratio of the age-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs), or equivalent, relating (continuous and categorical) BMI to coronary heart disease.
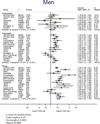
Findings: We reviewed a total of 8561 original entries twice for inclusion in the analysis, of which 32 published studies were eligible for inclusion. Data from 95 cohorts, 1,219,187 participants, and 37,488 incident cases of coronary heart disease were included. Higher BMI was significantly associated with age-adjusted coronary heart disease: for a one-unit (kg/m(2)) increment in BMI; the HR was 1·04 (95% CI 1·03-1·05) in women and 1·05 (1·04-1·07) in men. Compared with people of a normal weight, the age-adjusted HR of coronary heart disease for the underweight group was 1·25 (1·05-1·49) in women and 1·09 (0·91-1·23) in men; for the overweight group 1·20 (1·12-1·29) in women and 1·22 (1·12-1·32) in men; and for the obese group 1·61 (1·42-1·82) in women and 1·60 (1·43-1·79) in men. Overall, these associations did not differ between the sexes. The women-to-men ratios of the HRs were 0·99 (95% CI 0·98-1·00) for a one-unit increment in BMI, 1·10 (0·91-1·32) for the underweight group, 0·99 (0·92-1·07) for the overweight group, and 1·06 (0·95-1·17) for the obese group, relative to the normal weight group. Similar results were obtained after multiple adjustment and in a range of sensitivity analyses.
Interpretation: Increased BMI, measured either continuously or categorically, has the same deleterious effects on the risk of coronary heart disease in women and men across diverse populations.
Funding: None.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Comment in
-
BMI and coronary heart disease: no difference according to sex.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015 Jun;3(6):398-400. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00103-5. Epub 2015 May 7. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25960159 No abstract available.
References
* References of included studies
-
- Singh PN, Lindsted KD, Fraser GE. Body weight and mortality among adults who never smoked. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;150:1152–1164. - PubMed
-
- Woodward M, Barzi F, Martiniuk A, et al. Cohort profile: the Asia Pacific Cohort Studies Collaboration. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2006;35:1412–1416. - PubMed
-
- The Aric Investigators. The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study: design and objectives. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1989;129:687–702. - PubMed
-
- Dorn JM, Schisterman EF, Winkelstein W, Jr, Trevisan M. Body mass index and mortality in a general population sample of men and women. The Buffalo Health Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;146:919–931. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL079891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL079891/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

