Latent TGF-β-binding proteins
- PMID: 25960419
- PMCID: PMC4844006
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2015.05.005
Latent TGF-β-binding proteins
Abstract
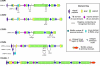
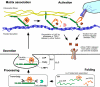
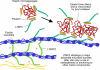
The LTBPs (or latent transforming growth factor β binding proteins) are important components of the extracellular matrix (ECM) that interact with fibrillin microfibrils and have a number of different roles in microfibril biology. There are four LTBPs isoforms in the human genome (LTBP-1, -2, -3, and -4), all of which appear to associate with fibrillin and the biology of each isoform is reviewed here. The LTBPs were first identified as forming latent complexes with TGFβ by covalently binding the TGFβ propeptide (LAP) via disulfide bonds in the endoplasmic reticulum. LAP in turn is cleaved from the mature TGFβ precursor in the trans-golgi network but LAP and TGFβ remain strongly bound through non-covalent interactions. LAP, TGFβ, and LTBP together form the large latent complex (LLC). LTBPs were originally thought to primarily play a role in maintaining TGFβ latency and targeting the latent growth factor to the extracellular matrix (ECM), but it has also been shown that LTBP-1 participates in TGFβ activation by integrins and may also regulate activation by proteases and other factors. LTBP-3 appears to have a role in skeletal formation including tooth development. As well as having important functions in TGFβ regulation, TGFβ-independent activities have recently been identified for LTBP-2 and LTBP-4 in stabilizing microfibril bundles and regulating elastic fiber assembly.
Keywords: Extracellular matrix; Latency associated protein; Latent TGFβ binding proteins; TGFβ activation.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Ali M, McKibbin M, Booth A, Parry DA, Jain P, Riazuddin SA, Hejtmancik JF, Khan SN, Firasat S, Shires M, Gilmour DF, Towns K, Murphy A-L, Azmanov D, Tournev I, Cherninkova S, Jafri H, Raashid Y, Toomes C, Craig J, Mackey DA, Kalaydjieva L, Riazuddin S, Inglehearn CF. Null mutations in LTBP2 cause primary congenital glaucoma. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84(5):664–671. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson SB, Goldberg AL, Whitman M. Identification of a novel pool of extracellular promyostatin in skeletal muscle. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2008;283(11):7027–7035. - PubMed
-
- Bai Y, Zhang P, Zhang X, Huang J, Hu S, Wei Y. LTBP-2 acts as a novel marker in human heart failure - a preliminary study. Biomarkers. 2012;17(5):407–415. - PubMed
-
- Bellusci S, Henderson R, Winnier G, Oikawa T, Hogan BL. Evidence from normal expression and targeted misexpression that bone morphogenetic protein (Bmp-4) plays a role in mouse embryonic lung morphogenesis. Development. 1996;122(6):1693–1702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

