NT-proBNP as early marker of subclinical late cardiotoxicity after doxorubicin therapy and mediastinal irradiation in childhood cancer survivors
- PMID: 25960594
- PMCID: PMC4415620
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/513219
NT-proBNP as early marker of subclinical late cardiotoxicity after doxorubicin therapy and mediastinal irradiation in childhood cancer survivors
Abstract
Background: Childhood cancer survivors treated with anthracyclines and mediastinal irradiation are at risk for late onset cardiotoxicity.
Aims of the study: To assess the role of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) as early predictors of late onset cardiotoxicity in asymptomatic survivors of childhood cancer treated with doxorubicin with or without mediastinal irradiation.
Methods: A cross-sectional study on 58 asymptomatic survivors of childhood cancer who received doxorubicin in their treatment protocols and 32 asymptomatic Hodgkin's lymphoma survivors who received anthracycline and mediastinal irradiation. Levels of NT-proBNP, TDI, and conventional echocardiography were determined.
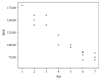
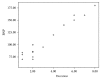
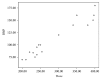
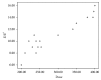
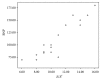
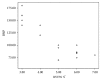
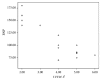
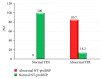
Results: Thirty percent of survivors had abnormal NT-proBNP levels. It was significantly related to age at diagnosis, duration of follow-up, and cumulative dose of doxorubicin. TDI detected myocardial affection in 20% more than conventional echocardiography. Furthermore, abnormalities in TDI and NT-pro-BNP levels were more common in Hodgkin lymphoma survivors receiving both chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Conclusions: TDI could detect early cardiac dysfunction even in those with normal conventional echocardiography. Measurement of NT-proBNP represents an interesting strategy for detecting subclinical cardiotoxicity. We recommend prospective and multicenter studies to validate the role of NT-proBNP as an early marker for late onset doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomarkers and early detection of late onset anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in children.Hematology. 2012 May;17(3):151-6. doi: 10.1179/102453312X13376952196412. Hematology. 2012. PMID: 22664114
-
The utility of NT-proBNP and various echocardiographic methods in the determination of doxorubicin induced subclinical late cardiotoxicity.Kardiol Pol. 2013;71(1):40-6. Kardiol Pol. 2013. PMID: 23348532
-
Abnormal NT-pro-BNP levels in asymptomatic long-term survivors of childhood cancer treated with anthracyclines.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009 May;52(5):631-6. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21913. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19127569
-
Biomarkers to diagnose ventricular dysfunction in childhood cancer survivors: a systematic review.Heart. 2019 Feb;105(3):210-216. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2018-313634. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Heart. 2019. PMID: 30158136
-
Clinical implications of B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro--B-type natriuretic peptide in the care of the vascular surgery patient.Semin Vasc Surg. 2014 Dec;27(3-4):143-7. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2015.01.004. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Semin Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 26073822 Review.
Cited by
-
Reply to Letter to the Editor: "Can ARNI Prevent Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity?".Anatol J Cardiol. 2022 Apr;26(4):344. doi: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2021.1371. Anatol J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35435851 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Efficacy and safety of cardioprotective drugs in chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: an updated systematic review & network meta-analysis.Cardiooncology. 2023 Feb 18;9(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40959-023-00159-0. Cardiooncology. 2023. PMID: 36804940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-Terminal Pro Brain Natriuretic Peptide, sST2, and Galectin-3 Levels in Breast Cancer Survivors.J Clin Med. 2021 Jul 27;10(15):3313. doi: 10.3390/jcm10153313. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34362097 Free PMC article.
-
Use of speckle tracking in the evaluation of late subclinical myocardial damage in survivors of childhood acute leukaemia.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Sep;34(9):1373-1381. doi: 10.1007/s10554-018-1346-9. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29611048
-
Potential roles of 4HNE-adducted protein in serum extracellular vesicles as an early indicator of oxidative response against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats.Curr Res Toxicol. 2023 Nov 3;5:100134. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2023.100134. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37964944 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

