Copeptin testing in acute myocardial infarction: ready for routine use?
- PMID: 25960596
- PMCID: PMC4415476
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/614145
Copeptin testing in acute myocardial infarction: ready for routine use?
Abstract
Suspected acute myocardial infarction is one of the leading causes of admission to emergency departments. In the last decade, biomarkers revolutionized the management of patients with suspected acute coronary syndromes. Besides their pivotal assistance in timely diagnosis, biomarkers provide additional information for risk stratification. Cardiac troponins I and T are the most sensitive and specific markers of acute myocardial injury. Nonetheless, in order to overcome the remaining limitations of these markers, novel candidate biomarkers sensitive to early stage of disease are being extensively investigated. Among them, copeptin, a stable peptide derived from the precursor of vasopressin, emerged as a promising biomarker for the evaluation of suspected acute myocardial infarction. In this review, we summarize the currently available evidence for the usefulness of copeptin in the diagnosis and risk stratification of patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction in comparison with routine biomarkers.
Figures
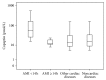
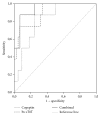
References
-
- Thygesen K., Alpert J. S., Jaffe A. S., et al. Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. European Heart Journal. 2012;33(20):2551–2567. - PubMed
-
- Hamm C. W., Bassand J.-P., Agewall S., et al. ESC guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute coronary syndromes (ACS) in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) European Heart Journal. 2011;32(23):2999–3054. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr236. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

