Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a woman with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
- PMID: 25960654
- PMCID: PMC4411014
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S84010
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a woman with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Abstract
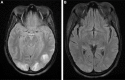
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a rare syndrome characterized by reversible vasogenic edema in the posterior hemispheres. PRES is most often attributed to primary hypertension, pre-eclampsia, and neurotoxicity secondary to immunosuppressants such as cyclosporine. Renal disease is an infrequent cause of PRES with a majority of cases occurring in adults with complete renal failure or in pediatric cases with underlying renal parenchymal disease and concurrent immunosuppressive therapy. Typical symptoms include seizure, headache, altered mental status, and visual disturbances. PRES is rarely associated with cerebral hemorrhage, and even less so with subarachnoid bleeds. Herein we report on a 25-year-old female with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis who developed PRES. The patient's presentation was more severe as she presented with seizure, nephrotic syndrome, and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging with concurrent symptoms led us to the final diagnosis. The patient was treated with antihypertensives, diuretics, and corticosteroids and follow-up imaging revealed resolution of PRES. Our case illustrates that underlying kidney disease even without immunosuppressive agents should be added to the list of possible causes for PRES. Symptoms are reversible with treatment of underlying cause or offending agent.
Keywords: PRES; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children complicated by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome.J Int Med Res. 2018 Mar;46(3):1172-1177. doi: 10.1177/0300060517746559. Epub 2018 Jan 8. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29310486 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Obstructive Hydrocephalus Due to Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Successfully Treated With Continuous Ventricular Drainage: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Mar 18;17(3):e80803. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80803. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40255820 Free PMC article.
-
[Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003 Nov-Dec;131(11-12):461-6. doi: 10.2298/sarh0312461p. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2003. PMID: 15114789 Serbian.
-
Late postpartum eclampsia complicated with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a case report and a literature review.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015 Dec;5(6):909-16. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4292.2015.12.04. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2015. PMID: 26807372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021 Feb 25;25(3):19. doi: 10.1007/s11916-020-00932-1. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2021. PMID: 33630183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome induced by food poisoning in a pediatric patient: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2020 Dec;48(12):300060520980201. doi: 10.1177/0300060520980201. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33349079 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible postoperative vision loss (POVL): A tale of four patients.Qatar Med J. 2024 Oct 7;2024(3):37. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2024.37. eCollection 2024. Qatar Med J. 2024. PMID: 39429722 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroid therapy and severity of vasogenic edema in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Sep 15;380:11-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.06.044. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28870548 Free PMC article.
-
From Gut to Gray Matter: A Case Report of Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Pediatric Patient With Celiac Disease.Clin Case Rep. 2025 Mar 20;13(3):e70260. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.70260. eCollection 2025 Mar. Clin Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40114993 Free PMC article.
-
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children complicated by posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome.J Int Med Res. 2018 Mar;46(3):1172-1177. doi: 10.1177/0300060517746559. Epub 2018 Jan 8. J Int Med Res. 2018. PMID: 29310486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sadek AR, Waters RJ, Sparrow OC. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a case following reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome masquerading as subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2012;154(3):413–416. - PubMed
-
- Lee VH, Wijdicks EF, Manno EM, Rabinstein AA. Clinical spectrum of reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. Arch Neurol. 2008;65(2):205–210. - PubMed
-
- Loar RW, Patterson MC, O’Leary PW, Driscoll DJ, Johnson JN. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and hemorrhage associated with tacrolimus in a pediatric heart transplantation recipient. Pediatr Transplant. 2013;17(2):E67–E70. - PubMed
-
- Pereira PR, Pinho J, Rodrigues M, et al. Clinical, imagiological and etiological spectrum of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Arg Neuropsiquiatr. 2015;73(1):36–40. - PubMed
-
- Landtblom AM, Fridriksson S, Boivie J, Hillman J, Johansson G, Johansson I. Sudden onset headache: a prospective study of features, incidence and causes. Cephalalgia. 2002;22(5):354–360. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

