Progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint for overall survival in patients with third-line or later-line chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer
- PMID: 25960663
- PMCID: PMC4410904
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S82365
Progression-free survival as a surrogate endpoint for overall survival in patients with third-line or later-line chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: The correlation between overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) has been evaluated in patients with metastatic or advanced gastric cancer who have received first-line and/or second-line chemotherapy. However, no corresponding analysis has been done for patients who have undergone third-line or later-line chemotherapy.
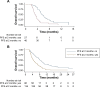
Methods: A total of 303 patients from the Phase II/III studies of apatinib were pooled (the Phase II study as a training data set, the Phase III study as a testing data set). Landmark analyses of PFS at 2 months from randomization were performed to minimize lead time bias. The Cox proportional hazard model was used to test for the significance effect of PFS rate at 2 months in predicting OS. Additionally, the PFS/OS correlations were evaluated by the normal induced copula (National Institute for Health and Care Excellence) estimation model.
Results: The median OS was 3.37 months (95% confidence interval 2.63-3.80) in patients who experienced progression at 2 months and 5.67 months in patients who did not (95% confidence interval 4.83-6.67; P<0.0001). Compared with patients who did not progress at 2 months, the adjusted hazard ratio for death was 3.39 (95% confidence interval 1.79-6.41; P<0.0001) for patients who experienced progression at 2 months. Moreover, the correlation of PFS/OS was 0.84 (95% confidence interval 0.74-0.90). Similar results were found in the testing data set.
Conclusion: These results indicate that PFS correlates strongly with OS, suggesting PFS may be a useful early endpoint for patients with advanced gastric cancer who have undergone third-line or later-line chemotherapy. These observations require prospective validation.
Keywords: gastric cancer; overall survival; progression-free survival; surrogate endpoint.
Figures
References
-
- Stewart BW, Wild CP. World Cancer Report 2014. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2014. [Accessed March 25, 2015]. Available from: http://www.iarc.fr/en/publications/pdfs-online/wcr/ - PubMed
-
- Kang YK, Kang WK, Shin DB, et al. Capecitabine/cisplatin versus 5-fluorouracil/cisplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a randomised phase III noninferiority trial. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:666–673. - PubMed
-
- Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, et al. S-1 plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:215–221. - PubMed
-
- Ajani JA, Buyse M, Lichinitser M, et al. Combination of cisplatin/S-1 in the treatment of patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: results of noninferiority and safety analyses compared with cisplatin/5-fluorouracil in the First-Line Advanced Gastric Cancer Study. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:3616–3624. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:687–697. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources