MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer
- PMID: 25960691
- PMCID: PMC4424445
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-015-0185-1
MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer
Abstract
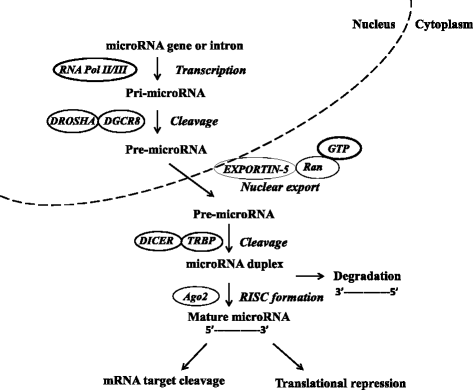
In recent years, there has been a tremendous and growing interest among researchers to investigate the role of mircoRNA (miRNA) in normal cellular as well as in disease processes. miRNAs are a family of small non-coding RNAs which were reported to regulate the expression of various oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. The expression profiling of miRNAs has already entered into cancer clinics as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers to assess tumor initiation, progression and response to treatment in cancer patients. This review summarizes: (i) the current understanding of interactions between miRNAs and their target genes, (ii) recent advances in the regulatory mechanisms that control the expression of genes related to carcinogenesis, and (iii) the role of miRNAs in cancer diagnosis and therapy.
Keywords: Cancer; DNA methylation; Diagnosis; Single nucleotide polymorphism; Therapy; miRNA.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

