Giant malignant insulinoma
- PMID: 25960993
- PMCID: PMC4422883
- DOI: 10.4174/astr.2015.88.5.289
Giant malignant insulinoma
Abstract
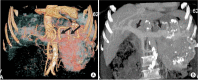
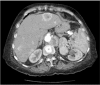
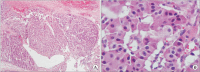
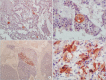
Insulinomas are the most common pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Most insulinomas are benign, small, intrapancreatic solid tumors and only large tumors have a tendency for malignancy. Most patients present with symptoms of hypoglycemia that are relieved with the administration of glucose. We herein present the case of a 75-year-old woman who presented with an acute hypoglycemic episode. Subsequent laboratory and radiological studies established the diagnosis of a 17-cm malignant insulinoma, with local invasion to the left kidney, lymph node metastasis, and hepatic metastases. Patient symptoms, diagnostic and imaging work-up and surgical management of both the primary and the metastatic disease are reviewed.
Keywords: Giant tumor; Insulinoma; PNET.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Service FJ, McMahon MM, O'Brien PC, Ballard DJ. Functioning insulinoma--incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival of patients: a 60-year study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1991;66:711–719. - PubMed
-
- Mansour JC, Chen H. Pancreatic endocrine tumors. J Surg Res. 2004;120:139–161. - PubMed
-
- Vinik AI, Woltering EA, Warner RR, Caplin M, O'Dorisio TM, Wiseman GA, et al. NANETS consensus guidelines for the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumor. Pancreas. 2010;39:713–734. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

