CT-Definable Subtypes of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Statement of the Fleischner Society
- PMID: 25961632
- PMCID: PMC4613878
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2015141579
CT-Definable Subtypes of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Statement of the Fleischner Society
Abstract
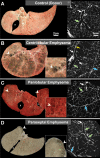
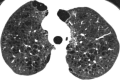
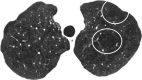
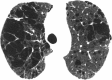
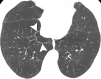
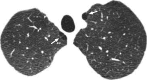
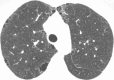
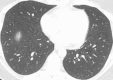
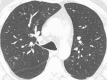
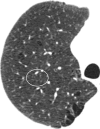
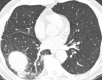
The purpose of this statement is to describe and define the phenotypic abnormalities that can be identified on visual and quantitative evaluation of computed tomographic (CT) images in subjects with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), with the goal of contributing to a personalized approach to the treatment of patients with COPD. Quantitative CT is useful for identifying and sequentially evaluating the extent of emphysematous lung destruction, changes in airway walls, and expiratory air trapping. However, visual assessment of CT scans remains important to describe patterns of altered lung structure in COPD. The classification system proposed and illustrated in this article provides a structured approach to visual and quantitative assessment of COPD. Emphysema is classified as centrilobular (subclassified as trace, mild, moderate, confluent, and advanced destructive emphysema), panlobular, and paraseptal (subclassified as mild or substantial). Additional important visual features include airway wall thickening, inflammatory small airways disease, tracheal abnormalities, interstitial lung abnormalities, pulmonary arterial enlargement, and bronchiectasis.
(©) RSNA, 2015.
Figures




References
-
- Petty TL, Weinmann GG. Building a national strategy for the prevention and management of and research in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Workshop Summary. Bethesda, Maryland, August 29–31, 1995. JAMA 1997;277(3):246–253. - PubMed
-
- Fabbri LM, Hurd SS; GOLD Scientific Committee. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD: 2003 update. Eur Respir J 2003;22(1):1–2. - PubMed
-
- Friedlander AL, Lynch D, Dyar LA, Bowler RP. Phenotypes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. COPD 2007;4(4):355–384. - PubMed
-
- Klein JS, Gamsu G, Webb WR, Golden JA, Müller NL. High-resolution CT diagnosis of emphysema in symptomatic patients with normal chest radiographs and isolated low diffusing capacity. Radiology 1992;182(3):817–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

