High glucose induces bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell senescence by upregulating autophagy
- PMID: 25961745
- PMCID: PMC4427318
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126537
High glucose induces bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell senescence by upregulating autophagy
Abstract
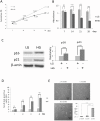
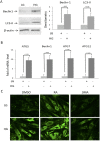
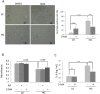
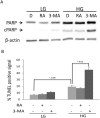
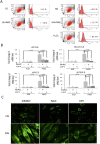
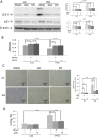
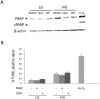
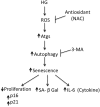
Hyperglycemia was reported to cause bone marrow hematopoietic niche dysfunction, and high glucose (HG) in the cultured medium induces MSC senescence. The underlying mechanism is unclear. Here, we investigated the role of HG-induced autophagy in bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) senescence. HG (25 mM) increased expression of Beclin-1, Atg 5, 7 and 12, generation of LC3-II and autophagosome formation which was correlated with development of cell senescence. Pretreatment of HG-MSC with 3-methyladenine (3-MA) prevented senescence but increased apoptosis. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) was effective in abrogating HG-induced autophagy accompanied by prevention of senescence. Diphenyleneiodonium (DPI), an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase, blocked autophagy and senescence in a manner comparable to NAC. 3-MA, NAC and DPI inhibited HG-induced interleukin-6 production in BMSCs. These results suggest that hyperglycemia induces MSC senescence and local inflammation via a novel oxidant-mediated autophagy which contributes to bone marrow niche dysfunction and hematopoietic impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Stolzing A, Coleman N, Scutt A (2006) Glucose-induced replicative senescence in mesenchymal stem cells. Rejuvenation Res 9(1): 31–35. - PubMed
-
- Parsch D, Fellenberg J, Brümmendorf TH, Eschlbeck AM, Richter W (2004) Telomere length and telomerase activity during expansion and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes. J Mol Med 82(1): 49–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

