Humic Acid Increases Amyloid β-Induced Cytotoxicity by Induction of ER Stress in Human SK-N-MC Neuronal Cells
- PMID: 25961951
- PMCID: PMC4463654
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms160510426
Humic Acid Increases Amyloid β-Induced Cytotoxicity by Induction of ER Stress in Human SK-N-MC Neuronal Cells
Abstract
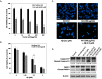
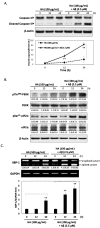
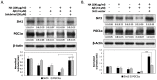
Humic acid (HA) is a possible etiological factor associated with for several vascular diseases. It is known that vascular risk factors can directly increase the susceptibility to Alzheimer's disease (AD), which is a neurodegenerative disorder due to accumulation of amyloid β (Aβ) peptide in the brain. However, the role that HA contributes to Aβ-induced cytotoxicity has not been demonstrated. In the present study, we demonstrate that HA exhibits a synergistic effect enhancing Aβ-induced cytotoxicity in cultured human SK-N-MC neuronal cells. Furthermore, this deterioration was mediated through the activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by stimulating PERK and eIF2α phosphorylation. We also observed HA and Aβ-induced cytotoxicity is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction caused by down-regulation of the Sirt1/PGC1α pathway, while in contrast, treating the cells with the ER stress inhibitor Salubrinal, or over-expression of Sirt1 significantly reduced loss of cell viability by HA and Aβ. Our findings suggest a new mechanism by which HA can deteriorate Aβ-induced cytotoxicity through modulation of ER stress, which may provide significant insights into the pathogenesis of AD co-occurring with vascular injury.
Figures




References
-
- Schulten H.R., Schnitzer M. A state of the art structural concept for humic substances. Naturwissenschaften. 1993;80:29–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01139754. - DOI
-
- Schmidt G., Pesch R., Schröder W., Conrad A., Kolossa-Gehring M., Feigenspan S., Dobler L., Wiesmüller G.A., Birke M., Utermann J. The potential of spatial information in human biomonitoring by example of two German environmental epidemiology studies. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2011;33:399–408. doi: 10.1007/s10653-011-9383-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gau R.J., Yang H.L., Suen J.L., Lu F.J. Induction of oxidative stress by humic acid through increasing intracellular iron: A possible mechanism leading to atherothrombotic vascular disorder in blackfoot disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001;283:743–749. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4832. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

