Small Heat Shock Protein Beta-1 (HSPB1) Is Upregulated and Regulates Autophagy and Apoptosis of Renal Tubular Cells in Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 25962073
- PMCID: PMC4427334
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126229
Small Heat Shock Protein Beta-1 (HSPB1) Is Upregulated and Regulates Autophagy and Apoptosis of Renal Tubular Cells in Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
Background: Heat shock protein beta-1 (HSPB1, also known as HSP27) is a small heat shock protein involved in many cellular processes and reportedly protects cells against oxidative stress. Autophagy protects cells from many types of stress and is thought to play a key role in preventing stress in acute kidney injury (AKI). However, little is known about the role of HSPB1 in autophagy and apoptosis in the pathogenesis of AKI.
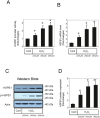
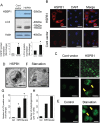
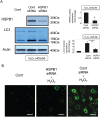
Methods: We used a rat ischemia/reperfusion AKI model and cultured renal tubular cells as an in vitro model. To elucidate the regulation of HSPB1, we evaluated the promoter activity and expression of HSPB1 in normal rat kidney (NRK)-52E cells in the presence of H2O2. To examine the regulation of autophagy by HSPB1, we established NRK-light chain 3 (NRK-LC3) cells that were stably transfected with a fusion protein of green fluorescent protein and LC3.
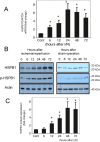
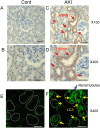
Results: The results of immunohistological examination showed that HSPB1 was expressed in proximal tubule cells after AKI. Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis showed that HSPB1 messenger RNA and protein expression were upregulated 6-72 h and 12-72 h, respectively, after ischemia/reperfusion injury. HSPB1 promoter activity as well as messenger RNA and protein expression indicated dose-dependent induction by H2O2. HSPB1 overexpression-induced autophagy in NRK-LC3 cells under normoxic conditions was confirmed with confocal microscopy, which revealed the presence of LC3-positive granules. Furthermore, H2O2-induced autophagy was inhibited by the transfection of small interfering RNAs for HSPB1. Overexpression of HSPB1 reduced BAX activation and H2O2-induced apoptosis, as measured by caspase 3 activity and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labeling assay.
Conclusions: We showed that HSPB1 expression increased during oxidative stress in AKI. Incremental HSPB1 expression increased autophagic flux and inhibited apoptosis in renal tubular cells. These results indicate that HSPB1 upregulation plays a role in the pathophysiology of AKI.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Devarajan P (2006) Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1503–1520. - PubMed
-
- Bonventre J V (2003) Dedifferentiation and proliferation of surviving epithelial cells in acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:S55–61. - PubMed
-
- Wallin A, Zhang G, Jones TW, Jaken S, Stevens J. (1992) Mechanism of the nephrogenic repair response. Studies on proliferation and vimentin expression after 35S-1, 2-dichlorovinyl-L-cysteine nephrotoxicity in vivo and in cultured proximal tubule epithelial cells. Lab Invest 66:474–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

