4'-O-methylhonokiol increases levels of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol in mouse brain via selective inhibition of its COX-2-mediated oxygenation
- PMID: 25962384
- PMCID: PMC4490613
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-015-0307-7
4'-O-methylhonokiol increases levels of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol in mouse brain via selective inhibition of its COX-2-mediated oxygenation
Abstract
Background and purpose: 4'-O-methylhonokiol (MH) is a natural product showing anti-inflammatory, anti-osteoclastogenic, and neuroprotective effects. MH was reported to modulate cannabinoid CB2 receptors as an inverse agonist for cAMP production and an agonist for intracellular [Ca2+]. It was recently shown that MH inhibits cAMP formation via CB2 receptors. In this study, the exact modulation of MH on CB2 receptor activity was elucidated and its endocannabinoid substrate-specific inhibition (SSI) of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and CNS bioavailability are described for the first time.
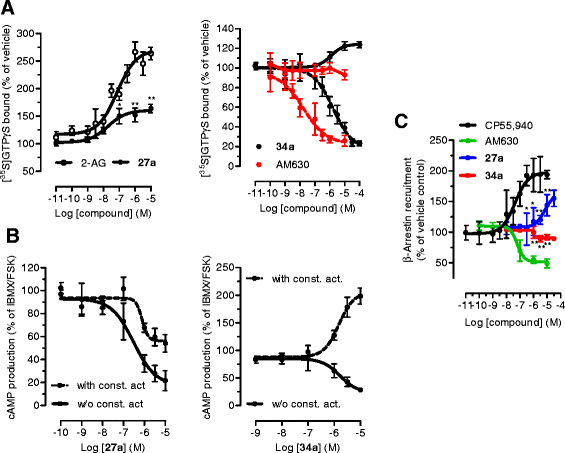
Methods: CB2 receptor modulation ([35S]GTPγS, cAMP, and β-arrestin) by MH was measured in hCB2-transfected CHO-K1 cells and native conditions (HL60 cells and mouse spleen). The COX-2 SSI was investigated in RAW264.7 cells and in Swiss albino mice by targeted metabolomics using LC-MS/MS.
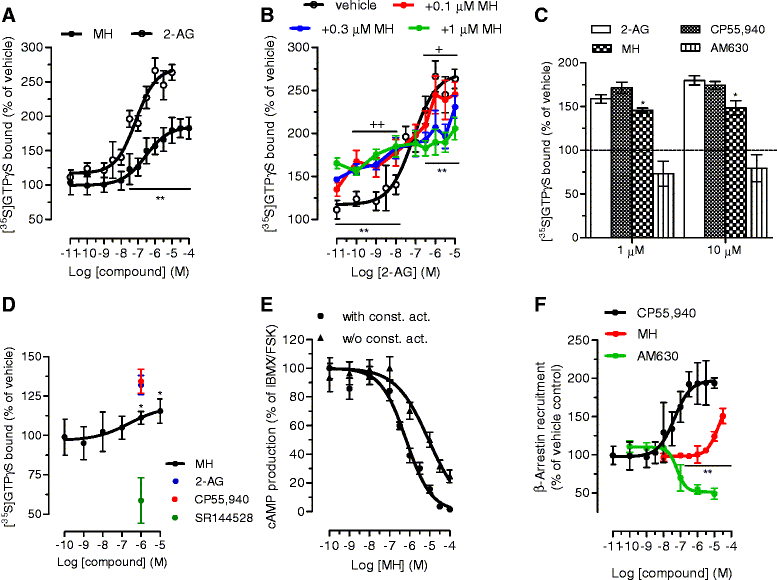
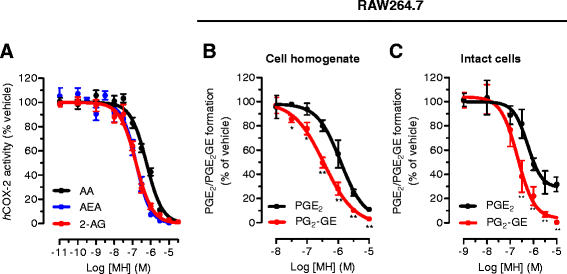
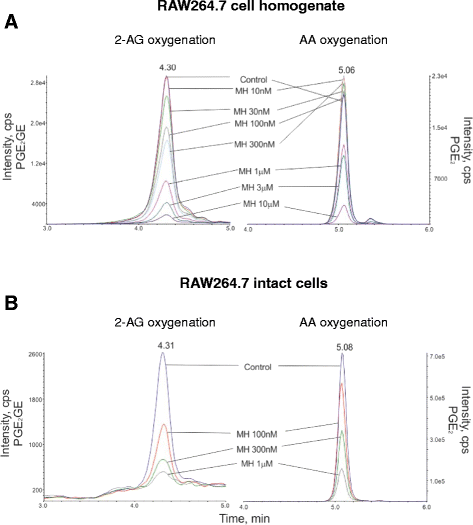
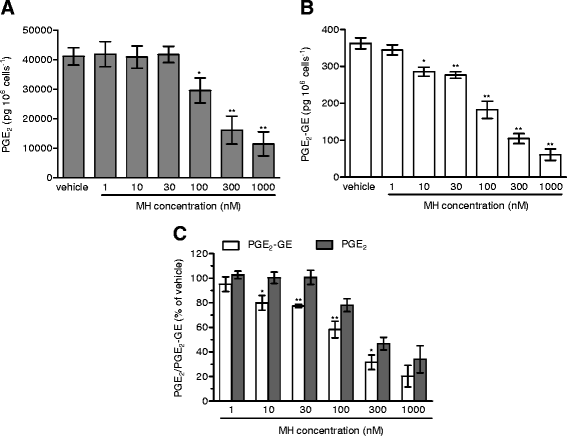
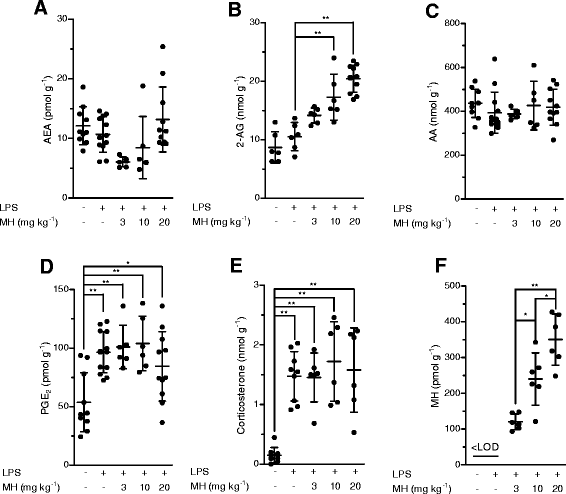
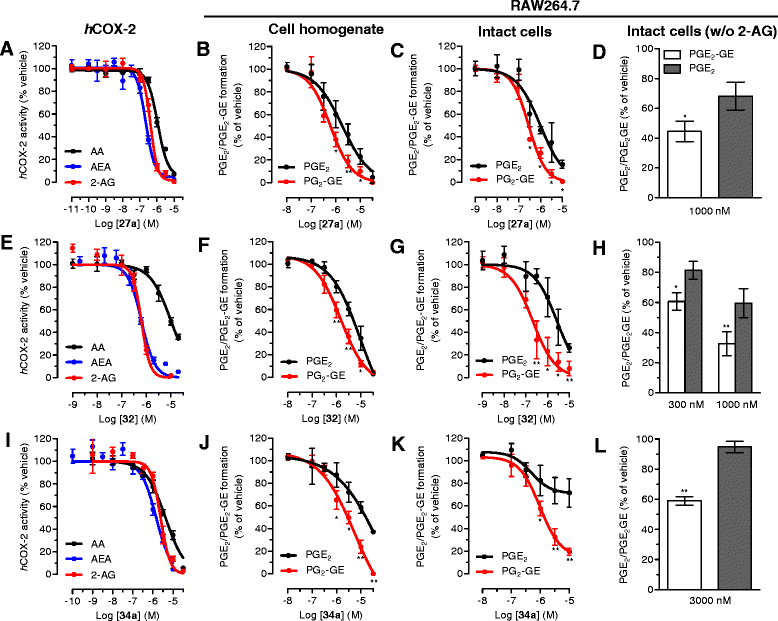
Results: MH is a CB2 receptor agonist and a potent COX-2 SSI. It induced partial agonism in both the [35S]GTPγS binding and β-arrestin recruitment assays while being a full agonist in the cAMP pathway. MH selectively inhibited PGE2 glycerol ester formation (over PGE2) in RAW264.7 cells and significantly increased the levels of 2-AG in mouse brain in a dose-dependent manner (3 to 20 mg kg(-1)) without affecting other metabolites. After 7 h from intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection, MH was quantified in significant amounts in the brain (corresponding to 200 to 300 nM).
Conclusions: LC-MS/MS quantification shows that MH is bioavailable to the brain and under condition of inflammation exerts significant indirect effects on 2-AG levels. The biphenyl scaffold might serve as valuable source of dual CB2 receptor modulators and COX-2 SSIs as demonstrated by additional MH analogs that show similar effects. The combination of CB2 agonism and COX-2 SSI offers a yet unexplored polypharmacology with expected synergistic effects in neuroinflammatory diseases, thus providing a rationale for the diverse neuroprotective effects reported for MH in animal models.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endocannabinoid 2-arachidonyl glycerol is a full agonist through human type 2 cannabinoid receptor: antagonism by anandamide.Mol Pharmacol. 2000 May;57(5):1045-50. Mol Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10779390
-
WWL70 attenuates PGE2 production derived from 2-arachidonoylglycerol in microglia by ABHD6-independent mechanism.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Jan 10;14(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0783-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28086912 Free PMC article.
-
The antinociceptive triterpene β-amyrin inhibits 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) hydrolysis without directly targeting cannabinoid receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;167(8):1596-608. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02059.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22646533 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling 2-arachidonoylglycerol metabolism as an anti-inflammatory strategy.Drug Discov Today. 2014 Mar;19(3):295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Drug Discov Today. 2014. PMID: 23891880 Review.
-
Aspects of Prostaglandin Glycerol Ester Biology.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1161:77-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-21735-8_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31562623 Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies: New Insights and Therapeutic Potential.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 22;10(12):3000. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123000. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacology, Toxicity, Bioavailability, and Formulation of Magnolol: An Update.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 17;12:632767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.632767. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33815113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4-O-Methylhonokiol Influences Normal Cardiovascular Development in Medaka Embryo.Molecules. 2019 Jan 29;24(3):475. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030475. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30699965 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT3 activator honokiol ameliorates surgery/anesthesia-induced cognitive decline in mice through anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammatory in hippocampus.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Mar;25(3):355-366. doi: 10.1111/cns.13053. Epub 2018 Sep 17. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 30296006 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Cyclooxygenase-2-Derived Oxygenation Products of the Endogenous Cannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol in Mouse Brain.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Jul 18;9(7):1552-1559. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00499. Epub 2018 May 9. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29722963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee YJ, Choi DY, Choi IS, Kim KH, Kim YH, Kim HM, et al. Inhibitory effect of 4-O-methylhonokiol on lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis and memory impairment via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB in vitro and in vivo models. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:35. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-35. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee YJ, Choi DY, Lee YK, Lee YM, Han SB, Kim YH, et al. 4-O-methylhonokiol prevents memory impairment in the Tg2576 transgenic mice model of Alzheimer’s disease via regulation of β-secretase activity. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;29:677–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

