Structural analyses of the chromatin remodelling enzymes INO80-C and SWR-C
- PMID: 25964121
- PMCID: PMC4431590
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms8108
Structural analyses of the chromatin remodelling enzymes INO80-C and SWR-C
Abstract
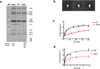
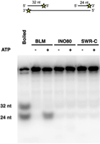
INO80-C and SWR-C are conserved members of a subfamily of ATP-dependent chromatin remodelling enzymes that function in transcription and genome-maintenance pathways. A crucial role for these enzymes is to control chromosomal distribution of the H2A.Z histone variant. Here we use electron microscopy (EM) and two-dimensional class averaging to demonstrate that these remodelling enzymes have similar overall architectures. Each enzyme is characterized by a dynamic 'tail' domain and a compact 'head' that contains Rvb1/Rvb2 subunits organized as hexameric rings. EM class averages and mass spectrometry support the existence of single heterohexameric rings in both SWR-C and INO80-C. EM studies define the position of the Arp8/Arp4/Act1 module within INO80-C, and we find that this module enhances nucleosome-binding affinity but is largely dispensable for remodelling activities. In contrast, the Ies6/Arp5 module is essential for INO80-C remodelling, and furthermore this module controls conformational changes that may couple nucleosome binding to remodelling.
Figures





References
-
- Clapier CR, Cairns BR. The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:273–304. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe S, Peterson CL. The INO80 family of chromatin-remodeling enzymes: regulators of histone variant dynamics. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Mizuguchi G, Shen X, Landry J, Wu WH, Sen S, Wu C. ATP-driven exchange of histone H2AZ variant catalyzed by SWR1 chromatin remodeling complex. Science. 2004;303:343–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

