Phase I Study of Single-Agent AZD1775 (MK-1775), a Wee1 Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients With Refractory Solid Tumors
- PMID: 25964244
- PMCID: PMC4606059
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.60.4009
Phase I Study of Single-Agent AZD1775 (MK-1775), a Wee1 Kinase Inhibitor, in Patients With Refractory Solid Tumors
Abstract
Purpose: Wee1 tyrosine kinase phosphorylates and inactivates cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) 1/2 in response to DNA damage. AZD1775 is a first-in-class inhibitor of Wee1 kinase with single-agent antitumor activity in preclinical models. We conducted a phase I study of single-agent AZD1775 in adult patients with refractory solid tumors to determine its maximum-tolerated dose (MTD), pharmacokinetics, and modulation of phosphorylated Tyr15-Cdk (pY15-Cdk) and phosphorylated histone H2AX (γH2AX) levels in paired tumor biopsies.
Patients and methods: AZD1775 was administered orally twice per day over 2.5 days per week for up to 2 weeks per 21-day cycle (3 + 3 design). At the MTD, paired tumor biopsies were obtained at baseline and after the fifth dose to determine pY15-Cdk and γH2AX levels. Six patients with BRCA-mutant solid tumors were also enrolled at the MTD.
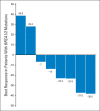
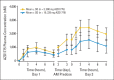
Results: Twenty-five patients were enrolled. The MTD was established as 225 mg twice per day orally over 2.5 days per week for 2 weeks per 21-day cycle. Confirmed partial responses were observed in two patients carrying BRCA mutations: one with head and neck cancer and one with ovarian cancer. Common toxicities were myelosuppression and diarrhea. Dose-limiting toxicities were supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and myelosuppression. Accumulation of drug (t1/2 approximately 11 hours) was observed. Reduction in pY15-Cdk levels (two of five paired biopsies) and increases in γH2AX levels (three of five paired biopsies) were demonstrated.
Conclusion: This is the first report of AZD1775 single-agent activity in patients carrying BRCA mutations. Proof-of-mechanism was demonstrated by target modulation and DNA damage response in paired tumor biopsies.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01748825.
© 2015 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures



Comment in
-
WEE1 Kinase As a Target for Cancer Therapy.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct 20;33(30):3485-7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.2290. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26215953 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hirai H, Arai T, Okada M, et al. MK-1775, a small molecule Wee1 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor efficacy of various DNA-damaging agents, including 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;9:514–522. - PubMed
-
- Hirai H, Iwasawa Y, Okada M, et al. Small-molecule inhibition of Wee1 kinase by MK-1775 selectively sensitizes p53-deficient tumor cells to DNA-damaging agents. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2992–3000. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

