Elucidation of G-protein and β-arrestin functional selectivity at the dopamine D2 receptor
- PMID: 25964346
- PMCID: PMC4460444
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1502742112
Elucidation of G-protein and β-arrestin functional selectivity at the dopamine D2 receptor
Abstract
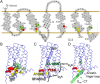
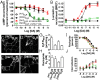
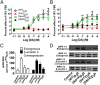
The neuromodulator dopamine signals through the dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) to modulate central nervous system functions through diverse signal transduction pathways. D2R is a prominent target for drug treatments in disorders where dopamine function is aberrant, such as schizophrenia. D2R signals through distinct G-protein and β-arrestin pathways, and drugs that are functionally selective for these pathways could have improved therapeutic potential. How D2R signals through the two pathways is still not well defined, and efforts to elucidate these pathways have been hampered by the lack of adequate tools for assessing the contribution of each pathway independently. To address this, Evolutionary Trace was used to produce D2R mutants with strongly biased signal transduction for either the G-protein or β-arrestin interactions. These mutants were used to resolve the role of G proteins and β-arrestins in D2R signaling assays. The results show that D2R interactions with the two downstream effectors are dissociable and that G-protein signaling accounts for D2R canonical MAP kinase signaling cascade activation, whereas β-arrestin only activates elements of this cascade under certain conditions. Nevertheless, when expressed in mice in GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the striatum, the β-arrestin-biased D2R caused a significant potentiation of amphetamine-induced locomotion, whereas the G protein-biased D2R had minimal effects. The mutant receptors generated here provide a molecular tool set that should enable a better definition of the individual roles of G-protein and β-arrestin signaling pathways in D2R pharmacology, neurobiology, and associated pathologies.
Keywords: G protein; GPCR; dopamine; functional selectivity; β-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.G.C. has received compensation from Lundbeck as a member of their Psychopharmacology Advisory Board and is a consultant for Omeros Corp. M.G.C. also owns equity in Acadia Pharmaceuticals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Receptor, Ligand and Transducer Contributions to Dopamine D2 Receptor Functional Selectivity.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 30;10(10):e0141637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141637. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26516769 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered D2R Variants Reveal the Balanced and Biased Contributions of G-Protein and β-Arrestin to Dopamine-Dependent Functions.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Apr;43(5):1164-1173. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.254. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29068002 Free PMC article.
-
The dopamine D2 receptor can directly recruit and activate GRK2 without G protein activation.J Biol Chem. 2018 Apr 20;293(16):6161-6171. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001300. Epub 2018 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29487132 Free PMC article.
-
New Concepts in Dopamine D2 Receptor Biased Signaling and Implications for Schizophrenia Therapy.Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 1;81(1):78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27832841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beta-arrestin signaling and regulation of transcription.J Cell Sci. 2007 Jan 15;120(Pt 2):213-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03338. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17215450 Review.
Cited by
-
Arrestin recruitment to dopamine D2 receptor mediates locomotion but not incentive motivation.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Sep;25(9):2086-2100. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0212-4. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 30120413 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Utility of Biased GPCR Signaling for Treatment of Psychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 29;20(13):3207. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133207. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Characterisation of the Mechanism of Action of Stimulant Drugs Lisdexamfetamine and Methylphenidate on ADHD Neurobiology: A Review.Neurol Ther. 2022 Dec;11(4):1489-1517. doi: 10.1007/s40120-022-00392-2. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Neurol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35951288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New phosphosite-specific antibodies to unravel the role of GRK phosphorylation in dopamine D2 receptor regulation and signaling.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 15;11(1):8288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87417-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33859231 Free PMC article.
-
The histamine H3 receptor modulates dopamine D2 receptor-dependent signaling pathways and mouse behaviors.J Biol Chem. 2023 Apr;299(4):104583. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104583. Epub 2023 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 36871761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjarnadóttir TK, et al. Comprehensive repertoire and phylogenetic analysis of the G protein-coupled receptors in human and mouse. Genomics. 2006;88(3):263–273. - PubMed
-
- Urban JD, et al. Functional selectivity and classical concepts of quantitative pharmacology. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;320(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Creese I, Burt DR, Snyder SH. Dopamine receptor binding predicts clinical and pharmacological potencies of antischizophrenic drugs. Science. 1976;192(4238):481–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

