Treatment with Vitamin D/MOG Association Suppresses Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 25965341
- PMCID: PMC4428830
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125836
Treatment with Vitamin D/MOG Association Suppresses Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Erratum in
-
Correction: Treatment with Vitamin D/MOG Association Suppresses Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 17;10(7):e0131260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131260. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26186539 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
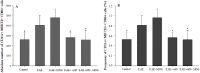
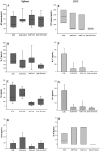
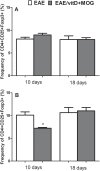
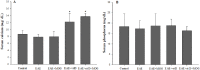
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an animal model to study multiple sclerosis (MS). Considering the tolerogenic effects of active vitamin D, we evaluated the therapeutic effect of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) associated with active vitamin D in EAE development. EAE was induced in female C57BL/6 mice by immunization with MOG emulsified with Complete Freund's Adjuvant plus Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Animals also received two intraperitoneal doses of Bordetella pertussis toxin. One day after immunization, mice were treated with 0,1 μg of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) every other day during 15 days (on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13 and 15). MOG (150 μg) was co-administered on days 3 and 11. The administration of 1,25(OH)2D3 or MOG determined significant reduction in EAE incidence and in clinical scores. When MOG was associated with 1,25(OH)2D3 the animals did not develop EAE. Spleen and central nervous system (CNS) cell cultures from this group produced less IL-6 and IL-17 upon stimulation with MOG in comparison to the EAE control group. In addition, this treatment inhibited dendritic cells maturation in the spleen and reduced inflammatory infiltration in the CNS. The association of MOG with 1,25(OH)2D3 was able to control EAE development.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Loleit V, Biberacher V, Hemmer B. Current and future therapies targeting the immune system in multiple sclerosis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15: 276–296. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell KM, Dotson AL, Cool KM, Chakrabarty A, Benedict SH, LeVine SM. Deferiprone, an orally deliverable iron chelator, ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mult Scler. 2007;13: 1118–1126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

