Balancing up and downregulation of the C. elegans X chromosomes
- PMID: 25966908
- PMCID: PMC4470837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2015.04.001
Balancing up and downregulation of the C. elegans X chromosomes
Abstract
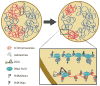
In Caenorhabditis elegans, males have one X chromosome and hermaphrodites have two. Emerging evidence indicates that the male X is transcriptionally more active than autosomes to balance the single X to two sets of autosomes. Because upregulation is not limited to males, hermaphrodites need to strike back and downregulate expression from the two X chromosomes to balance gene expression in their genome. Hermaphrodite-specific downregulation involves binding of the dosage compensation complex to both Xs. Advances in recent years revealed that the action of the dosage compensation complex results in compaction of the X chromosomes, changes in the distribution of histone modifications, and ultimately limiting RNA Polymerase II loading to achieve chromosome-wide gene repression.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
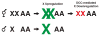
References
-
- Mank JE. Sex chromosome dosage compensation: definitely not for everyone. Trends Genet. 2013;29:677–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

