Uterine artery dysfunction in pregnant ACE2 knockout mice is associated with placental hypoxia and reduced umbilical blood flow velocity
- PMID: 25968580
- PMCID: PMC4490333
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00596.2014
Uterine artery dysfunction in pregnant ACE2 knockout mice is associated with placental hypoxia and reduced umbilical blood flow velocity
Abstract
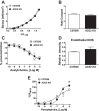
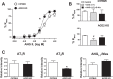
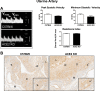
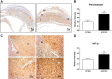
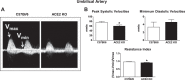
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) knockout is associated with reduced fetal weight at late gestation; however, whether uteroplacental vascular and/or hemodynamic disturbances underlie this growth-restricted phenotype is unknown. Uterine artery reactivity and flow velocities, umbilical flow velocities, trophoblast invasion, and placental hypoxia were determined in ACE2 knockout (KO) and C57Bl/6 wild-type (WT) mice at day 14 of gestation. Although systolic blood pressure was higher in pregnant ACE2 KO vs. WT mice (102.3 ± 5.1 vs. 85.1 ± 1.9 mmHg, n = 5-6), the magnitude of difference was similar to that observed in nonpregnant ACE2 KO vs. WT mice. Maternal urinary protein excretion, serum creatinine, and kidney or heart weights were not different in ACE2 KO vs. WT. Fetal weight and pup-to-placental weight ratio were lower in ACE2 KO vs. WT mice. A higher sensitivity to Ang II [pD2 8.64 ± 0.04 vs. 8.5 ± 0.03 (-log EC50)] and greater maximal contraction to phenylephrine (169.0 ± 9.0 vs. 139.0 ± 7.0% KMAX), were associated with lower immunostaining for Ang II receptor 2 and fibrinoid content of the uterine artery in ACE2 KO mice. Uterine artery flow velocities and trophoblast invasion were similar between study groups. In contrast, umbilical artery peak systolic velocities (60.2 ± 4.5 vs. 75.1 ± 4.5 mm/s) and the resistance index measured using VEVO 2100 ultrasound were lower in the ACE2 KO vs. WT mice. Immunostaining for pimonidazole, a marker of hypoxia, and hypoxia-inducible factor-2α were higher in the trophospongium and placental labyrinth of the ACE2 KO vs. WT. In summary, placental hypoxia and uterine artery dysfunction develop before major growth of the fetus occurs and may explain the fetal growth restricted phenotype.
Keywords: angiotensin II; fetal growth restriction; hypoxia; vascular reactivity; vasoconstriction.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander BT, Kassab SE, Miller MT, Abram SR, Reckelhoff JF, Bennett WA, Granger JP. Reduced uterine perfusion pressure during pregnancy in the rat is associated with increases in arterial pressure and changes in renal nitric oxide. Hypertension 37: 1191–1195, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Burrell JH, Lumbers ER. Angiotensin receptor subtypes in the uterine artery during ovine pregnancy. Eur J Pharmacol 330: 257–267, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Chen K, Merrill DC, Rose JC. The importance of angiotensin II subtype receptors for blood pressure control during mouse pregnancy. Reprod Sci 14: 694–704, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

