High-frequency voltage oscillations in cultured astrocytes
- PMID: 25969464
- PMCID: PMC4463829
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.12400
High-frequency voltage oscillations in cultured astrocytes
Abstract
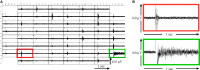
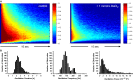
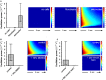
Because of their close interaction with neuronal physiology, astrocytes can modulate brain function in multiple ways. Here, we demonstrate a yet unknown astrocytic phenomenon: Astrocytes cultured on microelectrode arrays (MEAs) exhibited extracellular voltage fluctuations in a broad frequency spectrum (100-600 Hz) after electrical stimulation. These aperiodic high-frequency oscillations (HFOs) could last several seconds and did not spread across the MEA. The voltage-gated calcium channel antagonist cilnidipine dose-dependently decreased the power of the oscillations. While intracellular calcium was pivotal, incubation with bafilomycin A1 showed that vesicular release of transmitters played only a minor role in the emergence of HFOs. Gap junctions and volume-regulated anionic channels had just as little functional impact, which was demonstrated by the addition of carbenoxolone (100 μmol/L) and NPPB (100 μmol/L). Hyperpolarization with low potassium in the extracellular solution (2 mmol/L) dramatically raised oscillation power. A similar effect was seen when we added extra sodium (+50 mmol/L) or if we replaced it with NMDG(+) (50 mmol/L). The purinergic receptor antagonist PPADS suppressed the oscillation power, while the agonist ATP (100 μmol/L) had only an increasing effect when the bath solution pH was slightly lowered to pH 7.2. From these observations, we conclude that astrocytic voltage oscillations are triggered by activation of voltage-gated calcium channels and driven by a downstream influx of cations through channels that are permeable for large ions such as NMDG(+). Most likely candidates are subtypes of pore-forming P2X channels with a low affinity for ATP.
Keywords: Calcium channels; Glia; HFO; MEA; P2X channels; extracellular recording; multi‐electrode array; voltage oscillations.
© 2015 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American Physiological Society and The Physiological Society.
Figures


References
-
- Akita T, Fedorovich SV. Okada Y. Ca2+ nanodomain-mediated component of swelling-induced volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion current triggered by autocrine action of ATP in mouse astrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011;28:1181–1190. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CM, Bergher JP. Swanson RA. ATP-induced ATP release from astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2004;88:246–256. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

