Ezetimibe combined with standard diet and exercise therapy improves insulin resistance and atherosclerotic markers in patients with metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 25969718
- PMCID: PMC4420565
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12298
Ezetimibe combined with standard diet and exercise therapy improves insulin resistance and atherosclerotic markers in patients with metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Ezetimibe lowers serum lipid levels by inhibiting intestinal absorption of dietary and biliary cholesterol. However, the effect of ezetimibe on insulin resistance remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to examine this issue in patients with metabolic syndrome in local-dwelling Japanese, who were not being treated with lipid-lowering drugs.
Materials and methods: In 2009, 1,943 participants received a health examination in the Tanushimaru Study, a Japanese cohort of the Seven Countries Study, of whom 490 participants had metabolic syndrome. Among them, 61 participants (41 men and 20 women) were examined in the present study. They were treated with 10 mg of ezetimibe once a day for 24 weeks, combined with standard diet and exercise therapy.
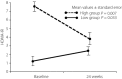
Results: Bodyweight (P < 0.001), body mass index (P < 0.001), systolic blood pressure (P = 0.003), diastolic blood pressure (P < 0.001), triglycerides (P = 0.002), non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (P = 0.001), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (P < 0.001) and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (P = 0.011) significantly decreased after the observational period. There were no statistically significant differences in the effects of ezetimibe between men and women. Univariate analysis showed that the reduction of homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance was not associated with the improvement of other metabolic components.
Conclusions: Ezetimibe combined with standard diet and exercise therapy improves not only bodyweight and atherogenic lipid profiles, but also insulin resistance, blood pressure and anthropometric factors in metabolic syndrome in local-dwelling Japanese. Interestingly, the improvement of insulin resistance had no correlation with other metabolic components.
Keywords: Ezetimibe; Insulin resistance; Metabolic syndrome.
Figures
References
-
- Knopp RH, Dujovne CA, Le Beaut A, et al. Ezetimibe Study Group. Evaluation of efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ezetimibe in primary hypercholesterolaemia: a pooled analysis from two controlled phase III clinical studies. Int J Clin Pract. 2003;57:363–368. - PubMed
-
- Denke M, Pearson T, Mcbride P, et al. Ezetimibe added to ongoing statin therapy improves LDL-C goal attainment and lipid profile in patients with diabetes or metabolic syndrome. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2006;3:93–102. - PubMed
-
- Hajer GR, Dallinga-Thie GM, van Vark-van der Zee LC, et al. The effect of statin alone or in combination with ezetimibe on postprandial lipoprotein composition in obese metabolic syndrome patients. Atherosclerosis. 2009;202:216–224. - PubMed
-
- Winkler K, Schewe T, Pütz G, et al. Fluvastatin/fenofibrate vs. simvastatin/ezetimibe in patients with metabolic syndrome: different effects on LDL-profiles. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009;39:463–470. - PubMed
-
- Robinson JG, Ballantyne CM, Grundy SM, et al. Lipid-altering efficacy and safety of ezetimibe/simvastatin versus atorvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia and the metabolic syndrome (from the VYMET Study) Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:1694–1702. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

