High-normal urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio is independently associated with metabolic syndrome in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional community-based study
- PMID: 25969722
- PMCID: PMC4420569
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12307
High-normal urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio is independently associated with metabolic syndrome in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional community-based study
Abstract
Aims/introduction: Microalbuminuria is positively related to metabolic syndrome (MetS). Our aim was to investigate whether urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) within the normal range is independently associated with MetS in Chinese community-based patients with type 2 diabetes.
Materials and methods: A total of 514 participants (206 males and 308 females; mean age 66 years) with UACR less than 3.5 mg/mmol were enrolled from two downtown areas of Shanghai. The participants were stratified into quartiles according to UACR levels. The prevalence of MetS was assessed and compared among the four groups by binary logistic regression.
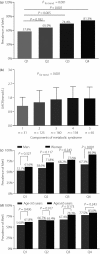
Results: Compared with participants with UACRs in the first quartile, the other quartiles had a higher prevalence of MetS (65.9%, 74.4% and 81.3%, respectively, P = 0.001) after adjustment for sex and age. After adjusting for potential confounders, participants in the second to the fourth quartile group had a 1.36-, 1.84- and 2.73-fold risk of MetS, respectively, relative to those in the lowest quartile. Furthermore, UACR, whether as quartile groups or as a continuous variable, is an independent predictor of MetS after fully adjusting for other variables.
Conclusions: These results suggest that UACR even within the normal range is independently associated with MetS in Chinese community-based patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Metabolic syndrome; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; Urinary-to-albumin creatinine ratio.
Figures
References
-
- Sulikowska B, Manitius J. Proteinuria as a predictor of risk of cardiovascular disease: a new insight. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2007;117:411–414. - PubMed
-
- Ishimura E, Taniwaki H, Tsuchida T, et al. Urinary albumin excretion associated with arterial wall stiffness rather than thickness in type 2 diabetic patients. J Nephrol. 2007;20:204–211. - PubMed
-
- Ito H, Komatsu Y, Mifune M, et al. The estimated GFR, but not the stage of diabetic nephropathy graded by the urinary albumin excretion, is associated with the carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2010;9:18. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

