Enhancement of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by endowing IgG with FcαRI (CD89) binding
- PMID: 25970007
- PMCID: PMC4623516
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1047570
Enhancement of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity by endowing IgG with FcαRI (CD89) binding
Abstract
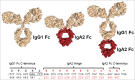
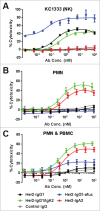
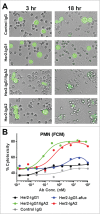
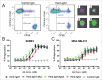
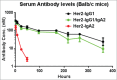
Fc effector functions such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) are crucial to the efficacy of many antibody therapeutics. In addition to IgG, antibodies of the IgA isotype can also promote cell killing through engagement of myeloid lineage cells via interactions between the IgA-Fc and FcαRI (CD89). Herein, we describe a unique, tandem IgG1/IgA2 antibody format in the context of a trastuzumab variable domain that exhibits enhanced ADCC and ADCP capabilities. The IgG1/IgA2 tandem Fc format retains IgG1 FcγR binding as well as FcRn-mediated serum persistence, yet is augmented with myeloid cell-mediated effector functions via FcαRI/IgA Fc interactions. In this work, we demonstrate anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 antibodies with the unique tandem IgG1/IgA2 Fc can better recruit and engage cytotoxic polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells than either the parental IgG1 or IgA2. Pharmacokinetics of IgG1/IgA2 in BALB/c mice are similar to the parental IgG, and far surpass the poor serum persistence of IgA2. The IgG1/IgA2 format is expressed at similar levels and with similar thermal stability to IgG1, and can be purified via standard protein A chromatography. The tandem IgG1/IgA2 format could potentially augment IgG-based immunotherapeutics with enhanced PMN-mediated cytotoxicity while avoiding many of the problems associated with developing IgAs.
Keywords: ADCC; ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; ADCP, antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis; AUC, area under the curve; CL, clearance rate; CD89; CDC, complement dependent cytotoxicity; Cmax, maximum serum concentration; DSC, differential scanning calorimetry; E:T ratio, effector to target ratio; FCM, flow cytometry; FcRn, neonatal Fc receptor; FcαRI; FcγR, Fc gamma receptor; HER2, human epithelial receptor two; IgA; IgA, immunoglobulin A; IgG, immunoglobulin G; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MΦ, macrophage; NK, natural killer; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cell; PK, pharmacokinetics; PMN, polymorphonuclear; SPR, surface plasmon resonance; TAA, tumor associated antigens; T½, half-life; Vss, central compartment volume of distribution; macrophage; monoclonal antibody; neutrophil; tandem; trastuzumab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FcalphaRI (CD89) as a novel trigger molecule for bispecific antibody therapy.Blood. 1997 Dec 1;90(11):4485-92. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9373259
-
Simultaneous Targeting of FcγRs and FcαRI Enhances Tumor Cell Killing.Cancer Immunol Res. 2015 Dec;3(12):1316-24. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0099-T. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 26407589
-
An engineered Fc variant of an IgG eliminates all immune effector functions via structural perturbations.Methods. 2014 Jan 1;65(1):114-26. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.06.035. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Methods. 2014. PMID: 23872058
-
Full-length recombinant antibodies from Escherichia coli: production, characterization, effector function (Fc) engineering, and clinical evaluation.MAbs. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2111748. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2022.2111748. MAbs. 2022. PMID: 36018829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Fc receptor for IgA (FcalphaRI, CD89).Immunol Lett. 2004 Mar 29;92(1-2):23-31. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2003.11.018. Immunol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15081523 Review.
Cited by
-
Multivalent IgM scaffold enhances the therapeutic potential of variant-agnostic ACE2 decoys against SARS-CoV-2.MAbs. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2212415. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2023.2212415. MAbs. 2023. PMID: 37229608 Free PMC article.
-
Fc Engineering Strategies to Advance IgA Antibodies as Therapeutic Agents.Antibodies (Basel). 2020 Dec 15;9(4):70. doi: 10.3390/antib9040070. Antibodies (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33333967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bi-isotype immunoglobulins enhance antibody-mediated neutrophil activity against Plasmodium falciparum parasites.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1360220. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1360220. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38650925 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin A Antibodies: From Protection to Harmful Roles.Immunol Rev. 2024 Nov;328(1):171-191. doi: 10.1111/imr.13424. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39578936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trispecific SEED antibodies engineered for neutrophil-mediated cell killing.MAbs. 2025 Dec;17(1):2532851. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2025.2532851. Epub 2025 Jul 15. MAbs. 2025. PMID: 40662295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weiner LM, Surana R, Wang S. Monoclonal antibodies: versatile platforms for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10:317-27; PMID:20414205; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nri2744 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iannello A, Ahmad A. Role of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the efficacy of therapeutic anti-cancer monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2005; 24:487-99; PMID:16408158; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10555-005-6192-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bulliard Y, Jolicoeur R, Zhang J, Dranoff G, Wilson NS, Brogdon JL. OX40 engagement depletes intratumoral Tregs via activating Fc[gamma]Rs, leading to antitumor efficacy. Immunol Cell Biol 2014; 92(6):475-80; PMID:24732076; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/icb.2014.26 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smyth MJ, Ngiow SF, Teng MWL. Targeting regulatory T cells in tumor immunotherapy. Immunol Cell Biol 2014; 92(6):473-4; PMID:24777313; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/icb.2014.33 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Satoh M, Iida S, Shitara K. Non-fucosylated therapeutic antibodies as next-generation therapeutic antibodies. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2006; 6:1161-73; PMID:17049014; http://dx.doi.org/10.1517/14712598.6.11.1161 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
