Targeted imaging of cancer by fluorocoxib C, a near-infrared cyclooxygenase-2 probe
- PMID: 25970082
- PMCID: PMC4430360
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JBO.20.5.050502
Targeted imaging of cancer by fluorocoxib C, a near-infrared cyclooxygenase-2 probe
Abstract
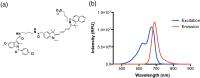
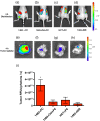
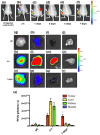
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is a promising target for the imaging of cancer in a range of diagnostic and therapeutic settings. We report a near-infrared COX-2-targeted probe, fluorocoxib C (FC), for visualization of solid tumors by optical imaging. FC exhibits selective and potent COX-2 inhibition in both purified protein and human cancercell lines. In vivo optical imaging shows selective accumulation of FC in COX-2-overexpressing human tumor xenografts [1483 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC)] implanted in nude mice, while minimal uptake is detectable in COX-2-negative tumor xenografts (HCT116)or 1483 HNSCC xenografts preblocked with the COX-2-selective inhibitor celecoxib. Time course imaging studies conducted from 3 h to 7-day post-FC injection revealed a marked reduction in nonspecific fluorescent signals with retention of fluorescence in 1483 HNSCC tumors. Thus, use of FC in a delayed imaging protocol offers an approach to improve imaging signal-to-noise that should improve cancer detection in multiple preclinical and clinical settings.
Figures
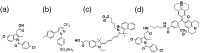
References
-
- Kubota R., et al. , “Microautoradiographic study for the differentiation of intratumoral macrophages, granulation tissues and cancer cells by the dynamics of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake,” J. Nucl. Med. 35(1), 104–112 (1994).JNMEAQ - PubMed
-
- Lowe V. J., et al. , “Optimum scanning protocol for FDG-PET evaluation of pulmonary malignancy,” J. Nucl. Med. 36(5), 883–887 (1995).JNMEAQ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

