A hybrid-membrane migration method to isolate high-purity adipose-derived stem cells from fat tissues
- PMID: 25970301
- PMCID: PMC4429558
- DOI: 10.1038/srep10217
A hybrid-membrane migration method to isolate high-purity adipose-derived stem cells from fat tissues
Abstract
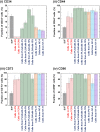
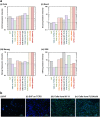
Human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) exhibit heterogeneous characteristics, indicating various genotypes and differentiation abilities. The isolated hADSCs can possess different purity levels and divergent properties depending on the purification methods used. We developed a hybrid-membrane migration method that purifies hADSCs from a fat tissue solution with extremely high purity and pluripotency. A primary fat-tissue solution was permeated through the porous membranes with a pore size from 8 to 25 μm, and the membranes were incubated in cell culture medium for 15-18 days. The hADSCs that migrated from the membranes contained an extremely high percentage (e.g., >98%) of cells positive for mesenchymal stem cell markers and showed almost one order of magnitude higher expression of some pluripotency genes (Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and Nanog) compared with cells isolated using the conventional culture method.
Figures


References
-
- Thomson J. A. et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282, 1145–1147 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K. et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 131, 861–872 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Higuchi A., Ling Q. D., Ko Y. A., Chang Y. & Umezawa A. Biomaterials for the feeder-free culture of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Chem. Rev. 111, 3021–3034 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Yu J. et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 318, 1917–1920 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Kim J. B. et al. Direct reprogramming of human neural stem cells by OCT4. Nature 461, 649–643 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

