Sharing and Specificity of Co-expression Networks across 35 Human Tissues
- PMID: 25970446
- PMCID: PMC4430528
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004220
Sharing and Specificity of Co-expression Networks across 35 Human Tissues
Abstract
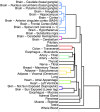
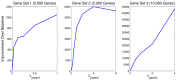
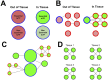
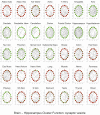
To understand the regulation of tissue-specific gene expression, the GTEx Consortium generated RNA-seq expression data for more than thirty distinct human tissues. This data provides an opportunity for deriving shared and tissue specific gene regulatory networks on the basis of co-expression between genes. However, a small number of samples are available for a majority of the tissues, and therefore statistical inference of networks in this setting is highly underpowered. To address this problem, we infer tissue-specific gene co-expression networks for 35 tissues in the GTEx dataset using a novel algorithm, GNAT, that uses a hierarchy of tissues to share data between related tissues. We show that this transfer learning approach increases the accuracy with which networks are learned. Analysis of these networks reveals that tissue-specific transcription factors are hubs that preferentially connect to genes with tissue specific functions. Additionally, we observe that genes with tissue-specific functions lie at the peripheries of our networks. We identify numerous modules enriched for Gene Ontology functions, and show that modules conserved across tissues are especially likely to have functions common to all tissues, while modules that are upregulated in a particular tissue are often instrumental to tissue-specific function. Finally, we provide a web tool, available at mostafavilab.stat.ubc.ca/GNAT, which allows exploration of gene function and regulation in a tissue-specific manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MH101822/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101819/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090936/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH090948/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH090941/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101820/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH101819/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004037/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA006227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH090937/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- N01MH000028/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101782/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH101814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA006227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA033684/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH101810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH090936/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH101825/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101825/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090948/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090941/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- DA033684/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- MH090951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101822/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH101820/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH101782/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090937/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

