Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase and Resistance to mTOR Inhibition in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
- PMID: 25971297
- PMCID: PMC4554194
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djv123
Targeting Focal Adhesion Kinase and Resistance to mTOR Inhibition in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors
Abstract
Background: Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) mediates survival of normal pancreatic islets through activation of AKT. Upon malignant transformation of islet cells into pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs), AKT is frequently overexpressed and mutations in the AKT/mTOR pathway are detected. Because mTOR inhibitors rarely induce PanNET tumor regression, partly because of feedback activation of AKT, novel combination strategies are needed to target FAK/AKT/mTOR signaling.
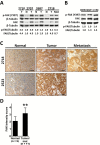
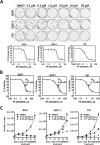
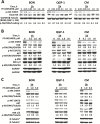
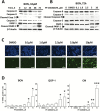
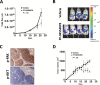
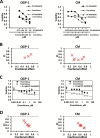
Methods: We characterized the activation of FAK in PanNETs using immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis and tested the FAK inhibitor PF-04554878 in human PanNET cells in vitro and in vivo (at least three mice per group). In addition, we evaluated the effect of combined FAK and mTOR inhibition on PanNET viability and apoptosis. All statistical tests were two-sided.
Results: We found that FAK is overexpressed and hyperphosphorylated in human PanNETs and that PF-04554878 strongly inhibited FAK (Tyr397) autophosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. We found that PF-04554878 inhibited cell proliferation and clonogenicity and induced apoptosis in PanNET cells. Moreover, oral administration of PF-04554878 statistically significantly reduced tumor growth in a patient-derived xenograft model of PanNET (P = .02) and in a human PanNET xenograft model of peritoneal carcinomatosis (P = .03). Importantly, PF-04554878 synergized with the mTOR inhibitor everolimus by preventing feedback AKT activation.
Conclusions: We demonstrate for the first time that FAK is overexpressed in PanNETs and that inhibition of FAK activity induces apoptosis and inhibits PanNET proliferation. We found that the novel FAK inhibitor PF-04554878 synergizes with everolimus, a US Food and Drug Administration-approved agent for PanNETs. Our findings warrant the clinical investigation of combined FAK and mTOR inhibition in PanNETs.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Sankhala K, Giles FJ. Potential of mTOR inhibitors as therapeutic agents in hematological malignancies. Expert Rev Hematol. 2009;2(4):399–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

