ERRγ target genes are poor prognostic factors in Tamoxifen-treated breast cancer
- PMID: 25971350
- PMCID: PMC4436109
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-015-0150-9
ERRγ target genes are poor prognostic factors in Tamoxifen-treated breast cancer
Abstract
Background: One-third of estrogen (ER+) and/or progesterone receptor-positive (PGR+) breast tumors treated with Tamoxifen (TAM) do not respond to initial treatment, and the remaining 70% are at risk to relapse in the future. Estrogen-related receptor gamma (ESRRG, ERRγ) is an orphan nuclear receptor with broad, structural similarities to classical ER that is widely implicated in the transcriptional regulation of energy homeostasis. We have previously demonstrated that ERRγ induces resistance to TAM in ER+ breast cancer models, and that the receptor's transcriptional activity is modified by activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway. We hypothesize that hyper-activation or over-expression of ERRγ induces a pro-survival transcriptional program that impairs the ability of TAM to inhibit the growth of ER+ breast cancer. The goal of the present study is to determine whether ERRγ target genes are associated with reduced distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) in ER+ breast cancer treated with TAM.
Methods: Raw gene expression data was obtained from 3 publicly available breast cancer clinical studies of women with ER+ breast cancer who received TAM as their sole endocrine therapy. ERRγ target genes were selected from 2 studies that published validated chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analyses of ERRγ promoter occupancy. Kaplan-Meier estimation was used to determine the association of ERRγ target genes with DMFS, and selected genes were validated in ER+, MCF7 breast cancer cells that express exogenous ERRγ.
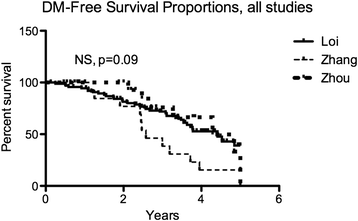
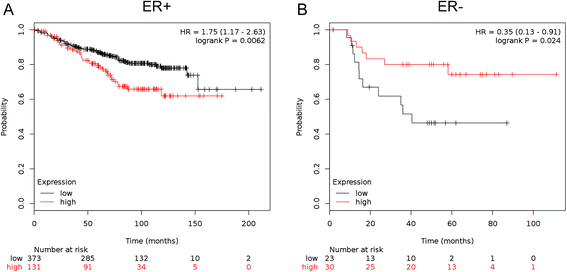
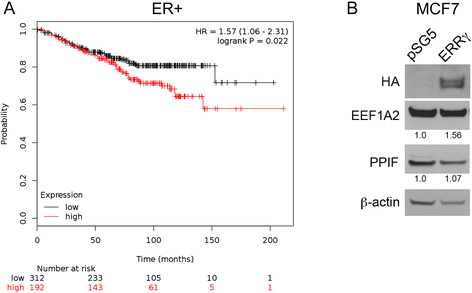
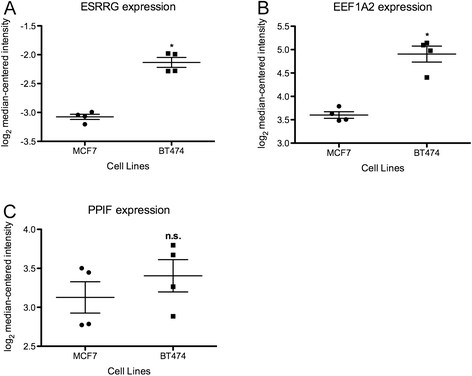
Results: Thirty-seven validated receptor target genes were statistically significantly altered in women who experienced a DM within 5 years, and could classify several independent studies into poor vs. good DMFS. Two genes (EEF1A2 and PPIF) could similarly separate ER+, TAM-treated breast tumors by DMFS, and their protein levels were measured in an ER+ breast cancer cell line model with exogenous ERRγ. Finally, expression of ERRγ and these two target genes are elevated in models of ER+ breast cancer with hyperactivation of ERK/MAPK.
Conclusions: ERRγ signaling is associated with poor DMFS in ER+, TAM-treated breast cancer, and ESRRG, EEF1A2, and PPIF comprise a 3-gene signaling node that may contribute to TAM resistance in the context of an active ERK/MAPK pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ERK/MAPK regulates ERRγ expression, transcriptional activity and receptor-mediated tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer.FEBS J. 2014 May;281(10):2431-42. doi: 10.1111/febs.12797. Epub 2014 Apr 28. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24684682 Free PMC article.
-
ERRgamma mediates tamoxifen resistance in novel models of invasive lobular breast cancer.Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;68(21):8908-17. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2669. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18974135 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004 Jun 16;96(12):926-35. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh166. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004. PMID: 15199112
-
Therapeutic targeting in the estrogen receptor hormonal pathway.Semin Oncol. 2004 Feb;31(1 Suppl 3):28-38. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2004.01.004. Semin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 15052541 Review.
-
Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance in the treatment of advanced breast cancer.Acta Oncol. 1996;35 Suppl 5:9-14. doi: 10.3109/02841869609083961. Acta Oncol. 1996. PMID: 9142958 Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated expression of PTCD3 correlates with tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis in patients with prostate cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Oct;18(4):3914-3922. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9402. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30132530 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-related receptor gamma functions as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer.Nat Commun. 2018 May 15;9(1):1920. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04244-2. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29765046 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine-induced ERRγ triggers chemoresistance of cancer cells through upregulation of ABCB1 and metabolic reprogramming.Theranostics. 2020 Feb 10;10(8):3382-3396. doi: 10.7150/thno.40144. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32206097 Free PMC article.
-
Sophoridine exerts tumor-suppressive activities via promoting ESRRG-mediated β-catenin degradation in gastric cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jun 22;20(1):582. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07067-x. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32571331 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of COX7RP and Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation in Breast Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 1;10:717881. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.717881. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35178385 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ebctcg: Early Breast Cancer Trialists Collaborative Group Systemic treatment of early breast cancer by hormonal, cytotoxic, or immune therapy. Lancet. 1992;399:1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

