Quercetin inhibits HGF/c-Met signaling and HGF-stimulated melanoma cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 25971889
- PMCID: PMC4435529
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-015-0367-4
Quercetin inhibits HGF/c-Met signaling and HGF-stimulated melanoma cell migration and invasion
Abstract
Background: Melanoma is notorious for its propensity to metastasize, which makes treatment extremely difficult. Receptor tyrosine kinase c-Met is activated in human melanoma and is involved in melanoma progression and metastasis. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-mediated activation of c-Met signaling has been suggested as a therapeutic target for melanoma metastasis. Quercetin is a dietary flavonoid that exerts anti-metastatic effect in various types of cancer including melanoma. In a previous report, we demonstrated that quercetin inhibited melanoma cell migration and invasion in vitro, and prevented melanoma cell lung metastasis in vivo. In this study, we sought to determine the involvement of HGF/c-Met signaling in the anti-metastatic action of quercetin in melanoma.
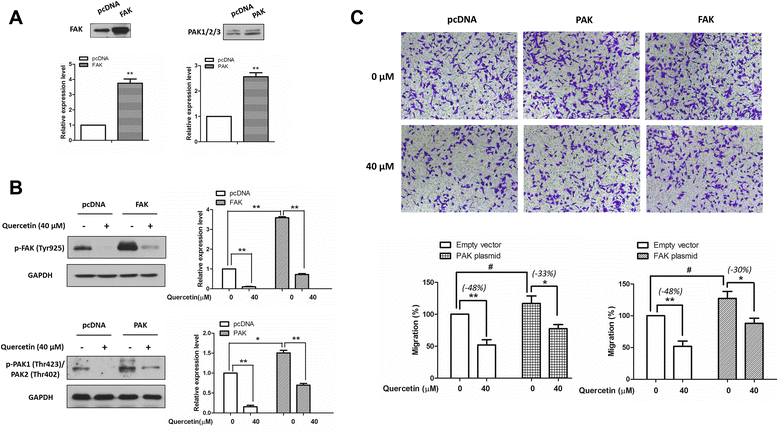
Methods: Transwell chamber assay was conducted to determine the cell migratory and invasive abilities. Western blotting was performed to determine the expression levels and activities of c-Met and its downstream molecules. And immunoblotting was performed in BS(3) cross-linked cells to examine the homo-dimerization of c-Met. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis was carried out to evaluate the mRNA expression level of HGF. Transient transfection was used to overexpress PAK or FAK in cell models. Student's t-test was used in analyzing differences between two groups.
Results: Quercetin dose-dependently suppressed HGF-stimulated melanoma cell migration and invasion. Further study indicated that quercetin inhibited c-Met phosphorylation, reduced c-Met homo-dimerization and decreased c-Met protein expression. The effect of quercetin on c-Met expression was associated with a reduced expression of fatty acid synthase. In addition, quercetin suppressed the phosphorylation of c-Met downstream molecules including Gab1 (GRB2-associated-binding protein 1), FAK (Focal Adhesion Kinase) and PAK (p21-activated kinases). More importantly, overexpression of FAK or PAK significantly reduced the inhibitory effect of quercetin on the migration of the melanoma cells.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that suppression of the HGF/c-Met signaling pathway contributes to the anti-metastatic action of quercetin in melanoma.
Figures




References
-
- Serrone L, Zeuli M, Sega FM, Cognetti F. Dacarbazine-based chemotherapy for metastatic melanoma: thirty-year experience overview. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2000;19:21–34. - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, Fisher RI, Weiss G, Margolin K, et al. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2105–2116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

