Specific Activation of the Plant P-type Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase by Lysophospholipids Depends on the Autoinhibitory N- and C-terminal Domains
- PMID: 25971968
- PMCID: PMC4481227
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.617746
Specific Activation of the Plant P-type Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase by Lysophospholipids Depends on the Autoinhibitory N- and C-terminal Domains
Abstract
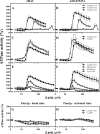
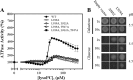
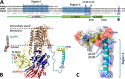
Eukaryotic P-type plasma membrane H(+)-ATPases are primary active transport systems that are regulated at the post-translation level by cis-acting autoinhibitory domains, which can be relieved by protein kinase-mediated phosphorylation or binding of specific lipid species. Here we show that lysophospholipids specifically activate a plant plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase (Arabidopsis thaliana AHA2) by a mechanism that involves both cytoplasmic terminal domains of AHA2, whereas they have no effect on the fungal counterpart (Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pma1p). The activation was dependent on the glycerol backbone of the lysophospholipid and increased with acyl chain length, whereas the headgroup had little effect on activation. Activation of the plant pump by lysophospholipids did not involve the penultimate residue, Thr-947, which is known to be phosphorylated as part of a binding site for activating 14-3-3 protein, but was critically dependent on a single autoinhibitory residue (Leu-919) upstream of the C-terminal cytoplasmic domain in AHA2. A corresponding residue is absent in the fungal counterpart. These data indicate that plant plasma membrane H(+)-ATPases evolved as specific receptors for lysophospholipids and support the hypothesis that lysophospholipids are important plant signaling molecules.
Keywords: H+-ATPase; lysophospholipid; plasma membrane; post-transcriptional regulation; proton pump.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Palmgren M. G. (2001) Plant plasma membrane H+-ATPases: powerhouses for nutrient uptake. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 52, 817–845 - PubMed
-
- Axelsen K. B., Palmgren M. G. (1998) Evolution of substrate specificities in the P-type ATPase superfamily. J. Mol. Evol. 46, 84–101 - PubMed
-
- Palmgren M. G., Nissen P. (2011) P-type ATPases. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 40, 243–266 - PubMed
-
- Sahoo S. K., Shaikh S. A., Sopariwala D. H., Bal N. C., Periasamy M. (2013) Sarcolipin protein interaction with sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) is distinct from phospholamban protein, and only sarcolipin can promote uncoupling of the SERCA pump. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 6881–6889 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

