The nicotinic α6 subunit gene determines variability in chronic pain sensitivity via cross-inhibition of P2X2/3 receptors
- PMID: 25972004
- PMCID: PMC5018401
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009986
The nicotinic α6 subunit gene determines variability in chronic pain sensitivity via cross-inhibition of P2X2/3 receptors
Abstract
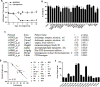
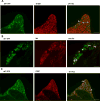
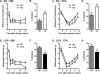
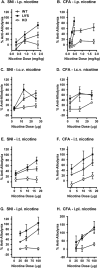
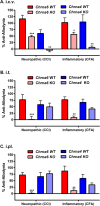
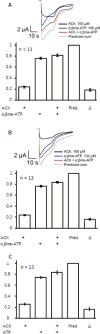
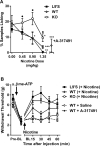
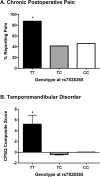
Chronic pain is a highly prevalent and poorly managed human health problem. We used microarray-based expression genomics in 25 inbred mouse strains to identify dorsal root ganglion (DRG)-expressed genetic contributors to mechanical allodynia, a prominent symptom of chronic pain. We identified expression levels of Chrna6, which encodes the α6 subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), as highly associated with allodynia. We confirmed the importance of α6* (α6-containing) nAChRs by analyzing both gain- and loss-of-function mutants. We find that mechanical allodynia associated with neuropathic and inflammatory injuries is significantly altered in α6* mutants, and that α6* but not α4* nicotinic receptors are absolutely required for peripheral and/or spinal nicotine analgesia. Furthermore, we show that Chrna6's role in analgesia is at least partially due to direct interaction and cross-inhibition of α6* nAChRs with P2X2/3 receptors in DRG nociceptors. Finally, we establish the relevance of our results to humans by the observation of genetic association in patients suffering from chronic postsurgical and temporomandibular pain.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Persson A-K, Gebauer M, Jordan S, Metz-Weidmann C, Schulte AM, Schneider H-C, Ding-Pfennigdorff D, Thun J, Xu X-J, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Darvasi A, Fried K, Devor M. Correlational analysis for identifying genes whose regulation contributes to chronic neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 2009;5:7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Persson A-K, Xu X-J, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Devor M, Fried K. Expression of DRG candidate pain molecules after nerve injury – a comparative study among five inbred mouse strains with contrasting pain phenotypes. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2010;15:26–39. - PubMed
-
- Nissenbaum J, Devor M, Seltzer Z, Gebauer M, Michaelis M, Tal M, Dorfman R, Abitbul-Yarkon M, Lu Y, Elahipanah T, delCanho S, Minert A, Fried K, Persson A-K, Shpigler H, Shabo E, Yakir B, Pisante A, Darvasi A. Susceptibility to chronic pain following nerve injury is genetically affected by CACNG2. Genome Res. 2010;20:1180–1190. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vincler M. Neuronal nicotinic receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Expert Opin Invest Drugs. 2005;14:1191–1198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

