Dysregulated RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC) Assembly within CNS Corresponds with Abnormal miRNA Expression during Autoimmune Demyelination
- PMID: 25972178
- PMCID: PMC6705439
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4794-14.2015
Dysregulated RNA-Induced Silencing Complex (RISC) Assembly within CNS Corresponds with Abnormal miRNA Expression during Autoimmune Demyelination
Abstract
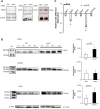
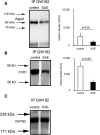
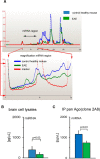
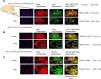
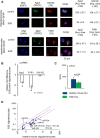
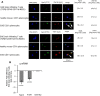
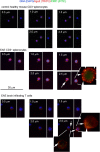
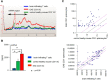
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) associate with Argonaute (Ago), GW182, and FXR1 proteins to form RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs). RISCs represent a critical checkpoint in the regulation and bioavailability of miRNAs. Recent studies have revealed dysregulation of miRNAs in multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE); however, the function of RISCs in EAE and MS is largely unknown. Here, we examined the expression of Ago, GW182, and FXR1 in CNS tissue, oligodendrocytes (OLs), brain-infiltrating T lymphocytes, and CD3(+)splenocytes (SCs) of EAE mic, and found that global RISC protein levels were significantly dysregulated. Specifically, Ago2 and FXR1 levels were decreased in OLs and brain-infiltrating T cells in EAE mice. Accordingly, assembly of Ago2/GW182/FXR1 complexes in EAE brain tissues was disrupted, as confirmed by immunoprecipitation experiments. In parallel with alterations in RISC complex content in OLs, we found downregulation of miRNAs essential for differentiation and survival of OLs and myelin synthesis. In brain-infiltrating T lymphocytes, aberrant RISC formation contributed to miRNA-dependent proinflammatory helper T-cell polarization. In CD3(+) SCs, we found increased expression of both Ago2 and FXR1 in EAE compared with nonimmunized mice. Therefore, our results demonstrate a gradient in expression of miRNA between primary activated T cells in the periphery and polarized CNS-infiltrating T cells. These results suggest that, in polarized autoreactive effector T cells, miRNA synthesis is inhibited in response to dysregulated RISC assembly, allowing these cells to maintain a highly specific proinflammatory program. Therefore, our findings may provide a mechanism that leads to miRNA dysregulation in EAE/MS.
Keywords: Ago proteins; EAE; RISC; miRNA.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/357521-17$15.00/0.
Figures

References
-
- Breving K, Esquela-Kerscher A. The complexities of microRNA regulation: mirandering around the rules. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:1316–1329. - PubMed
-
- Bronevetsky Y, Villarino AV, Eisley CJ, Barbeau R, Barczak AJ, Heinz GA, Kremmer E, Heissmeyer V, McManus MT, Erle DJ, Rao A, Ansel KM. T cell activation induces proteasomal degradation of Argonaute and rapid remodeling of the microRNA repertoire. J Exp Med. 2013;210:417–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.20111717. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
