IL-23/IL-17A Dysfunction Phenotypes Inform Possible Clinical Effects from Anti-IL-17A Therapies
- PMID: 25972190
- PMCID: PMC4580732
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2015.144
IL-23/IL-17A Dysfunction Phenotypes Inform Possible Clinical Effects from Anti-IL-17A Therapies
Abstract
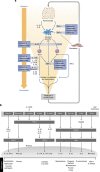
Biologics that neutralize specific cytokines have improved outcomes for several immune-mediated disorders but may also increase risks for particular side effects. This article postulates potential immunologic consequences of inhibiting components of the IL-23/T-helper cell 17 pathway-the target of next-generation biologics for treating psoriasis-based on clinical phenotypes of inherent or acquired deficiencies in this pathway. Generally, downstream deficiencies (e.g., IL-17A, IL-17F) are associated with fewer disorders compared with upstream deficiencies, suggesting that selectively blocking downstream targets may result in a narrower range of side effects. However, safety of these specific inhibitions must be established in long-term studies.
Figures
References
-
- Akahoshi M, Nakashima H, Miyake K et al. (2003) Influence of interleukin-12 receptor β1 polymorphisms on tuberculosis. Hum Genet 112:237–243 - PubMed
-
- Al-Muhsen S, Casanova JL. (2008) The genetic heterogeneity of Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122:1043–1503 - PubMed
-
- Altare F, Durandy A, Lammas D et al. (1998) Impairment of mycobacterial immunity in human interleukin-12 receptor deficiency. Science 280:1432–1435 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

