Salivary gland tumor fine-needle aspiration cytology: a proposal for a risk stratification classification
- PMID: 25972326
- PMCID: PMC5257286
- DOI: 10.1309/AJCPMII6OSD2HSJA
Salivary gland tumor fine-needle aspiration cytology: a proposal for a risk stratification classification
Abstract
Objectives: Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is useful in the evaluation of salivary gland tumors, but currently no standard terminology or risk stratification model exists.
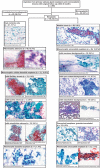
Methods: FNA smears were reviewed and categorized based on cytonuclear features, stromal characteristics, and background characteristics. Risk of malignancy was calculated for each category. Classifications as benign, neoplasm of uncertain malignant potential (NUMP), suspicious for malignancy, and positive for malignancy were used to aggregate categories into similar risk groups.
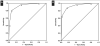
Results: Categorization of salivary gland aspirates into morphologic categories resulted in the expected risk stratification. Grouping of categories maintained risk stratification, providing classes with malignancy risk as follows: benign, 2%; NUMP, 18%; suspicious for malignancy, 76%; and positive for malignancy, 100%.
Conclusions: Salivary gland FNA categorization into commonly encountered morphologic categories provides risk stratification, which translates to a simplified classification scheme of benign, NUMP, suspicious, and positive for malignancy similar to the paradigm in other organ systems.
Keywords: Cytology; Fine-needle aspiration; Risk stratification; Salivary gland.
Copyright© by the American Society for Clinical Pathology.
Figures
References
-
- Schmidt RL, Hall BJ, Wilson AR, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration cytology for parotid gland lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;136:45–59. - PubMed
-
- Layfield LJ, Gopez E, Hirschowitz S. Cost efficiency analysis for fine-needle aspiration in the workup of parotid and submandibular gland nodules. Diagn Cytopathol. 2006;34:734–738. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt RL, Hunt JP, Hall BJ, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of frozen section for parotid gland lesions. Am J Clin Pathol. 2011;136:729–738. - PubMed
-
- Seethala RR, LiVolsi VA, Baloch ZW. Relative accuracy of fine-needle aspiration and frozen section in the diagnosis of lesions of the parotid gland. Head Neck. 2005;27:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Colella G, Cannavale R, Flamminio F, et al. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of salivary gland lesions: a systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68:2146–2153. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

