Defining the roles of arrestin2 and arrestin3 in vasoconstrictor receptor desensitization in hypertension
- PMID: 25972452
- PMCID: PMC4525080
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00079.2015
Defining the roles of arrestin2 and arrestin3 in vasoconstrictor receptor desensitization in hypertension
Abstract
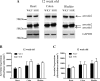
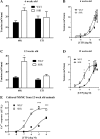
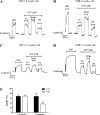
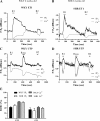
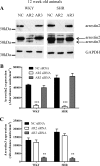
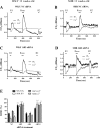
Prolonged vasoconstrictor-stimulated phospholipase C activity can induce arterial constriction, hypertension, and smooth muscle hypertrophy/hyperplasia. Arrestin proteins are recruited by agonist-occupied G protein-coupled receptors to terminate signaling and counteract changes in vascular tone. Here we determine whether the development of hypertension affects arrestin expression in resistance arteries and how such changes alter arterial contractile signaling and function. Arrestin2/3 expression was increased in mesenteric arteries of 12-wk-old spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) compared with normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) controls, while no differences in arrestin expression were observed between 6-wk-old SHR and WKY animals. In mesenteric artery myography experiments, high extracellular K(+)-stimulated contractions were increased in both 6- and 12-wk-old SHR animals. Concentration-response experiments for uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP) acting through P2Y receptors displayed a leftward shift in 12-wk, but not 6-wk-old animals. Desensitization of UTP-stimulated vessel contractions was increased in 12-wk-old (but not 6-wk-old) SHR animals. Dual IP3/Ca(2+) imaging in mesenteric arterial cells showed that desensitization of UTP and endothelin-1 (ET1) responses was enhanced in 12-wk-old (but not 6-wk-old) SHR compared with WKY rats. siRNA-mediated depletion of arrestin2 for UTP and arrestin3 for ET1, reversed the desensitization of PLC signaling. In conclusion, arrestin2 and 3 expression is elevated in resistance arteries during the emergence of the early hypertensive phenotype, which underlies an enhanced ability to desensitize vasoconstrictor signaling and vessel contraction. Such regulatory changes may act to compensate for increased vasoconstrictor-induced vessel contraction.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor; arrestin; hypertension; phospholipase C; resistance artery; vasoconstrictor.
Copyright © 2015 the American Physiological Society.
Figures



References
-
- Attramadal H, Arriza JL, Aoki C, Dawson TM, Codina J, Kwatra MM, Snyder SH, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. β-arrestin2, a novel member of the arrestin/β-arrestin gene family. J Biol Chem 267: 17882–17890, 1992. - PubMed
-
- DeFea KA. Arrestins in actin reorganization and cell migration. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 118: 205–222, 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

