Isolation, characterization, kinetics, and enzymatic and nonenzymatic microbicidal activities of a novel c-type lysozyme from plasma of Schistocerca gregaria (Orthoptera: Acrididae)
- PMID: 25972507
- PMCID: PMC4535491
- DOI: 10.1093/jisesa/iev038
Isolation, characterization, kinetics, and enzymatic and nonenzymatic microbicidal activities of a novel c-type lysozyme from plasma of Schistocerca gregaria (Orthoptera: Acrididae)
Abstract
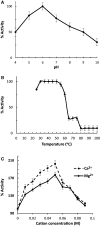
A protein, designated as Sgl, showing a muramidase lytic activity to the cell wall of the Gram-positive bacterium Micrococcus lysodeikticus was isolated for the first time from plasma of Escherichia coli-immunized fifth instar Schistocerca gregaria. The isolated Sgl was detected as a single protein band, on both native- and SDS-PAGE, has a molecular weight of ∼15.7 kDa and an isoelectric point (pI) of ca 9.3 and its antiserum has specifically recognized its isolated form. Fifty-nine percentage of Sgl lytic activity was recovered in the isolated fractions and yielded ca 126-fold increase in specific activity than that of the crude. The partial N-terminal amino acid sequence of the Sgl has 55 and 40% maximum identity with Bombyx mori and Gallus gallus c-type lysozymes, respectively. The antibacterial activity against the Gram-positive and the Gram-negative bacteria were comparatively stronger than that of the hen egg white lysozyme (HEWL). The detected Sgl poration to the inner membrane that reach a maximum ability after 3 h was suggested to operate as a nonenzymatic mechanism for Gram-negative bacterial cell lysis, as tested in a permease-deficient E. coli, ML-35 strain. Sgl showed a maximal muramidase activity at pH 6.2, 30-50°C, and 0.05 M Ca(2+) or Mg(2+); and has a Km of 0.5 μg/ml and a Vmax of 0.518 with M. lysodeikticus as a substrate. The Sgl displayed a chitinase activity against chitin with a Km of 0.93 mg/ml and a Vmax of 1.63.
Keywords: Schistocerca gregaria; antibacterial activity; kinetics; lysozyme c; muramidase.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Entomological Society of America.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of a c-type lysozyme from the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria (Orthoptera: Acrididae).Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 Aug;61:60-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.03.018. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26997372
-
Comparison of bactericidal activity of six lysozymes at atmospheric pressure and under high hydrostatic pressure.Int J Food Microbiol. 2006 May 1;108(3):355-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.11.021. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Int J Food Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16487612
-
Purification and partial characterization of an induced antibacterial protein in the silkworm, Bombyx mori.J Invertebr Pathol. 1995 Jan;65(1):17-24. doi: 10.1006/jipa.1995.1003. J Invertebr Pathol. 1995. PMID: 7876591
-
What is new in lysozyme research and its application in food industry? A review.Food Chem. 2019 Feb 15;274:698-709. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.017. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30372997 Review.
-
Can lysozymes mediate antibacterial resistance in plants?Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;23(1):209-14. doi: 10.1007/BF00021432. Plant Mol Biol. 1993. PMID: 8219050 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Expression Analysis Reveals the Association of Several Genes with Pupal Diapause in Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae).Insects. 2019 Jun 13;10(6):169. doi: 10.3390/insects10060169. Insects. 2019. PMID: 31200584 Free PMC article.
-
Insect immunology and hematopoiesis.Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 May;58:102-18. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2015.12.006. Epub 2015 Dec 13. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26695127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Immune Regulatory Role of Non-Coding RNAs (miRNAs and lncRNAs) in Insect-Pathogen Interactions.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 6;13:856457. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.856457. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35464405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of yolk formation, oviposition and egg quality of locust (Locusta migratoria manilensis) infected by Paranosema locustae.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 21;13:848267. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.848267. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35935997 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: the Achilles' Heel of Antibiotic Resistance?Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019 Jun;11(2):370-381. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9465-0. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019. PMID: 30229514 Review.
References
-
- Abraham E. G., Nagaraju J., Salunke D. M., Gupta H. M., Dutta R. K. 1995. Purification and partial characterization of an induced antibacterial protein in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J. Invert. Pathol. 65: 17–24. - PubMed
-
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris C., Turck M. 1966. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 45: 493–496. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

