AtmiRNET: a web-based resource for reconstructing regulatory networks of Arabidopsis microRNAs
- PMID: 25972521
- PMCID: PMC4429749
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bav042
AtmiRNET: a web-based resource for reconstructing regulatory networks of Arabidopsis microRNAs
Abstract
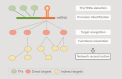
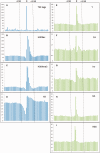
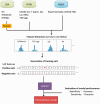
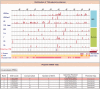
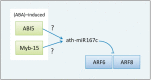
Compared with animal microRNAs (miRNAs), our limited knowledge of how miRNAs involve in significant biological processes in plants is still unclear. AtmiRNET is a novel resource geared toward plant scientists for reconstructing regulatory networks of Arabidopsis miRNAs. By means of highlighted miRNA studies in target recognition, functional enrichment of target genes, promoter identification and detection of cis- and trans-elements, AtmiRNET allows users to explore mechanisms of transcriptional regulation and miRNA functions in Arabidopsis thaliana, which are rarely investigated so far. High-throughput next-generation sequencing datasets from transcriptional start sites (TSSs)-relevant experiments as well as five core promoter elements were collected to establish the support vector machine-based prediction model for Arabidopsis miRNA TSSs. Then, high-confidence transcription factors participate in transcriptional regulation of Arabidopsis miRNAs are provided based on statistical approach. Furthermore, both experimentally verified and putative miRNA-target interactions, whose validity was supported by the correlations between the expression levels of miRNAs and their targets, are elucidated for functional enrichment analysis. The inferred regulatory networks give users an intuitive insight into the pivotal roles of Arabidopsis miRNAs through the crosstalk between miRNA transcriptional regulation (upstream) and miRNA-mediate (downstream) gene circuits. The valuable information that is visually oriented in AtmiRNET recruits the scant understanding of plant miRNAs and will be useful (e.g. ABA-miR167c-auxin signaling pathway) for further research. Database URL: http://AtmiRNET.itps.ncku.edu.tw/
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miRFANs: an integrated database for Arabidopsis thaliana microRNA function annotations.BMC Plant Biol. 2012 May 14;12:68. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-68. BMC Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22583976 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of microRNA regulatory modules in Arabidopsis via a probabilistic graphical model.Bioinformatics. 2009 Feb 1;25(3):387-93. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn626. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19056778
-
Prediction and identification of Arabidopsis thaliana microRNAs and their mRNA targets.Genome Biol. 2004;5(9):R65. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-9-r65. Epub 2004 Aug 31. Genome Biol. 2004. PMID: 15345049 Free PMC article.
-
Small Genetic Circuits and MicroRNAs: Big Players in Polymerase II Transcriptional Control in Plants.Plant Cell. 2016 Feb;28(2):286-303. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00852. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Plant Cell. 2016. PMID: 26869700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant and animal microRNAs: similarities and differences.Funct Integr Genomics. 2005 Jul;5(3):129-35. doi: 10.1007/s10142-005-0145-2. Epub 2005 May 5. Funct Integr Genomics. 2005. PMID: 15875226 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying and Characterizing the Circular RNAs during the Lifespan of Arabidopsis Leaves.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jul 20;8:1278. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01278. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28785273 Free PMC article.
-
Role of non-coding RNAs in quality improvement of horticultural crops: computational tools, databases, and algorithms for identification and analysis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Apr 4;25(1):80. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01592-3. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40183947 Review.
-
Methods of MicroRNA Promoter Prediction and Transcription Factor Mediated Regulatory Network.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7049406. doi: 10.1155/2017/7049406. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28656148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ascophyllum nodosum extract mitigates salinity stress in Arabidopsis thaliana by modulating the expression of miRNA involved in stress tolerance and nutrient acquisition.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 29;13(10):e0206221. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206221. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30372454 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of web-based resources of non-coding RNAs for plant science research.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 May 22;14(8):819-832. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24593. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29989090 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

