Forced Hepatic Overexpression of CEACAM1 Curtails Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 25972571
- PMCID: PMC4512217
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-1772
Forced Hepatic Overexpression of CEACAM1 Curtails Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance
Abstract
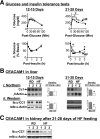
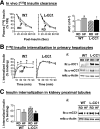
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (CEACAM1) regulates insulin sensitivity by promoting hepatic insulin clearance. Liver-specific inactivation or global null-mutation of Ceacam1 impairs hepatic insulin extraction to cause chronic hyperinsulinemia, resulting in insulin resistance and visceral obesity. In this study we investigated whether diet-induced insulin resistance implicates changes in hepatic CEACAM1. We report that feeding C57/BL6J mice a high-fat diet reduced hepatic CEACAM1 levels by >50% beginning at 21 days, causing hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, and elevation in hepatic triacylglycerol content. Conversely, liver-specific inducible CEACAM1 expression prevented hyperinsulinemia and markedly limited insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation that were induced by prolonged high-fat intake. This was partly mediated by increased hepatic β-fatty acid oxidation and energy expenditure. The data demonstrate that the high-fat diet reduced hepatic CEACAM1 expression and that overexpressing CEACAM1 in liver curtailed diet-induced metabolic abnormalities by protecting hepatic insulin clearance.
© 2015 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures




References
-
- Svedberg J, Björntorp P, Smith U, Lönnroth P. Free-fatty acid inhibition of insulin binding, degradation, and action in isolated rat hepatocytes. Diabetes 1990;39:570–574 - PubMed
-
- Osborne TF. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): key regulators of nutritional homeostasis and insulin action. J Biol Chem 2000;275:32379–32382 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK083850/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24-DK-093000/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112248/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-054254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-67536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-083850/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK093000/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103215/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DK-103215/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL-112248/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

