Repetitive hyperbaric oxygenation attenuates reactive astrogliosis and suppresses expression of inflammatory mediators in the rat model of brain injury
- PMID: 25972624
- PMCID: PMC4417949
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/498405
Repetitive hyperbaric oxygenation attenuates reactive astrogliosis and suppresses expression of inflammatory mediators in the rat model of brain injury
Abstract
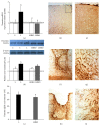
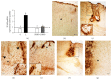
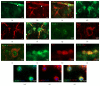
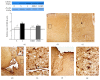
The exact mechanisms by which treatment with hyperbaric oxygen (HBOT) exerts its beneficial effects on recovery after brain injury are still unrevealed. Therefore, in this study we investigated the influence of repetitive HBOT on the reactive astrogliosis and expression of mediators of inflammation after cortical stab injury (CSI). CSI was performed on male Wistar rats, divided into control, sham, and lesioned groups with appropriate HBO. The HBOT protocol was as follows: 10 minutes of slow compression, 2.5 atmospheres absolute (ATA) for 60 minutes, and 10 minutes of slow decompression, once a day for 10 consecutive days. Data obtained using real-time polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, and immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence analyses revealed that repetitive HBOT applied after the CSI attenuates reactive astrogliosis and glial scarring, and reduces expression of GFAP (glial fibrillary acidic protein), vimentin, and ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule-1) both at gene and tissue levels. In addition, HBOT prevents expression of CD40 and its ligand CD40L on microglia, neutrophils, cortical neurons, and reactive astrocytes. Accordingly, repetitive HBOT, by prevention of glial scarring and limiting of expression of inflammatory mediators, supports formation of more permissive environment for repair and regeneration.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hyperbaric oxygenation alters temporal expression pattern of superoxide dismutase 2 after cortical stab injury in rats.Croat Med J. 2012 Dec;53(6):586-97. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2012.53.586. Croat Med J. 2012. PMID: 23275324 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hyperbaric oxygen on myelin injury and repair after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in adult rat.Neurosci Lett. 2023 Jan 18;794:137015. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2022.137015. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Neurosci Lett. 2023. PMID: 36526030
-
[Therapeutic efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen on traumatic brain injury in the rat and the underlying mechanisms].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Jan;28(1):42-6. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22493893 Chinese.
-
Hyperbaric oxygenation therapy alleviates chronic constrictive injury-induced neuropathic pain and reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production.Anesth Analg. 2011 Sep;113(3):626-33. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31821f9544. Epub 2011 May 19. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 21596875
-
Unestablished indications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy.Diving Hyperb Med. 2014 Dec;44(4):228-34. Diving Hyperb Med. 2014. PMID: 25596836 Review.
Cited by
-
A Dual Role for Hyperbaric Oxygen in Stroke Neuroprotection: Preconditioning of the Brain and Stem Cells.Cond Med. 2018 Jun;1(4):151-166. Cond Med. 2018. PMID: 30079404 Free PMC article.
-
The role of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in astrocytes during hyperoxia-induced brain injury.Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 25;74(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01984-4. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39862240 Review.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy versus placebo for post-concussion syndrome (HOT-POCS): A randomized, double-blinded controlled pilot study.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2023 Jun 20;34:101176. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101176. eCollection 2023 Aug. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2023. PMID: 37416626 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Alleviates Memory and Motor Impairments Following Traumatic Brain Injury via the Modulation of Mitochondrial-Dysfunction-Induced Neuronal Apoptosis in Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;12(12):2034. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122034. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136154 Free PMC article.
-
Inhalational Gases for Neuroprotection in Traumatic Brain Injury.J Neurotrauma. 2021 Oct 1;38(19):2634-2651. doi: 10.1089/neu.2021.0053. Epub 2021 Jun 8. J Neurotrauma. 2021. PMID: 33940933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pekovic S., Subasic S., Nedeljkovic N., et al. Molecular basis of brain injury and repair. In: Ruzdijic S., Rakic L., editors. Neurobiological Studies—From Genes to Behaviour. Kerala, India: Research Signpost; 2006. pp. 143–165.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

