Enhancing growth performance and systemic acquired resistance of medicinal plant Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under salt stress
- PMID: 25972748
- PMCID: PMC4423721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.03.004
Enhancing growth performance and systemic acquired resistance of medicinal plant Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr using arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi under salt stress
Abstract
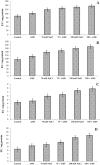
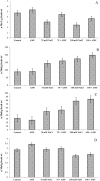
Pot experiments were conducted to evaluate the damaging effects of salinity on Sesbania sesban plants in the presence and absence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF). The selected morphological, physiological and biochemical parameters of S. sesban were measured. Salinity reduced growth and chlorophyll content drastically while as AMF inoculated plants improved growth. A decrease in the number of nodules, nodule weight and nitrogenase activity was also evident due to salinity stress causing reduction in nitrogen fixation and assimilation potential. AMF inoculation increased these parameters and also ameliorated the salinity stress to some extent. Antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and glutathione reductase (GR) as well as non enzymatic antioxidants (ascorbic acid and glutathione) also exhibited great variation with salinity treatment. Salinity caused great alterations in the endogenous levels of growth hormones with abscisic acid showing increment. AMF inoculated plants maintained higher levels of growth hormones and also allayed the negative impact of salinity.
Keywords: AMF; Nodulation; Salinity; Sesbania sesban; Systemic acquired resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott L.K., Robson A.D. Growth stimulation of subterranean clover with vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizas. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1977;28:639–649.
-
- Ahanger M.A., Hashem Abeer, Abd Allah E.F., Ahmad P. Arbuscular Mycorrhiza in crop improvement under environmental stress. In: Ahmad P., Rasool S., editors. vol. 2. Academic Press; USA: 2014. pp. 69–95. (Emerging Technologies and Management of Crop Stress Tolerance). ISBN-13: 978-0128008751.
-
- Ahmad P., Hakeem K.R., Kumar A., Ashraf M., Akram N.A. Salt-induced changes in photosynthetic activity and oxidative defense system of three cultivars of mustard (Brassica juncea L.) Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012;11:2694–2703.
-
- Ahmad P., Jaleel C.A., Salem M.A., Nabi G., Sharma S. Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2010;30:161–175. - PubMed
-
- Alexander, M., 1982. Most probable number method for microbial populations. In: Page, A.C., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, second ed., Chemical and Microbial Properties, Madison, USA., pp: 815–820.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

