Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the NPR1-like gene family from Persea americana (Mill.)
- PMID: 25972890
- PMCID: PMC4413732
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00300
Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the NPR1-like gene family from Persea americana (Mill.)
Abstract
The NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES1 (NPR1) forms an integral part of the salicylic acid (SA) pathway in plants and is involved in cross-talk between the SA and jasmonic acid/ethylene (JA/ET) pathways. Therefore, NPR1 is essential to the effective response of plants to pathogens. Avocado (Persea americana) is a commercially important crop worldwide. Significant losses in production result from Phytophthora root rot, caused by the hemibiotroph, Phytophthora cinnamomi. This oomycete infects the feeder roots of avocado trees leading to an overall decline in health and eventual death. The interaction between avocado and P. cinnamomi is poorly understood and as such limited control strategies exist. Thus uncovering the role of NPR1 in avocado could provide novel insights into the avocado - P. cinnamomi interaction. A total of five NPR1-like sequences were identified. These sequences were annotated using FGENESH and a maximum-likelihood tree was constructed using 34 NPR1-like protein sequences from other plant species. The conserved protein domains and functional motifs of these sequences were predicted. Reverse transcription quantitative PCR was used to analyze the expression of the five NPR1-like sequences in the roots of avocado after treatment with salicylic and jasmonic acid, P. cinnamomi infection, across different tissues and in P. cinnamomi infected tolerant and susceptible rootstocks. Of the five NPR1-like sequences three have strong support for a defensive role while two are most likely involved in development. Significant differences in the expression profiles of these five NPR1-like genes were observed, assisting in functional classification. Understanding the interaction of avocado and P. cinnamomi is essential to developing new control strategies. This work enables further classification of these genes by means of functional annotation and is a crucial step in understanding the role of NPR1 during P. cinnamomi infection.
Keywords: NPR1; Phytophthora cinnamomi; avocado; expression analysis; jasmonic acid; pathogenesis-related; salicylic acid.
Figures
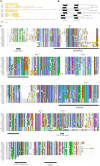

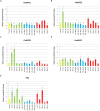


References
-
- Bekker T. F., Kaiser C., Labuschagne N. (2006). Efficacy of water soluble silicon against Phytophthora cinnamomi root rot of avocado: a progress report. S. Afr. Avocado Growers’ Assoc. Yearb. 29 58–62.
-
- Botha T., Kotze J. M. (1989). Exudates of avocado rootstocks and their possible role in resistance to Phytophthora cinnamomi. S. Afr. Avocado Growers’ Assoc. Yearb. 12 64–65.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

