Transcriptional control of stem cell fate by E2Fs and pocket proteins
- PMID: 25972892
- PMCID: PMC4412126
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00161
Transcriptional control of stem cell fate by E2Fs and pocket proteins
Abstract
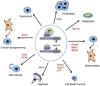
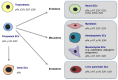
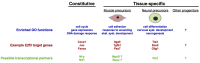
E2F transcription factors and their regulatory partners, the pocket proteins (PPs), have emerged as essential regulators of stem cell fate control in a number of lineages. In mammals, this role extends from both pluripotent stem cells to those encompassing all embryonic germ layers, as well as extra-embryonic lineages. E2F/PP-mediated regulation of stem cell decisions is highly evolutionarily conserved, and is likely a pivotal biological mechanism underlying stem cell homeostasis. This has immense implications for organismal development, tissue maintenance, and regeneration. In this article, we discuss the roles of E2F factors and PPs in stem cell populations, focusing on mammalian systems. We discuss emerging findings that position the E2F and PP families as widespread and dynamic epigenetic regulators of cell fate decisions. Additionally, we focus on the ever expanding landscape of E2F/PP target genes, and explore the possibility that E2Fs are not simply regulators of general 'multi-purpose' cell fate genes but can execute tissue- and cell type-specific gene regulatory programs.
Keywords: E2F transcription factors; cell cycle; epigenetics; neural precursor cell (NPC); pocket proteins; stem cell fate; stem cells; transcription.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tissue-specific targeting of cell fate regulatory genes by E2f factors.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Apr;23(4):565-75. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.36. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 25909886 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular transformation of mouse embryo fibroblasts in the absence of activator E2Fs.J Virol. 2015 May;89(9):5124-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03578-14. Epub 2015 Feb 25. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25717106 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving intricacies and implications of E2F1 regulation.FASEB J. 2003 Apr;17(6):569-74. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0431rev. FASEB J. 2003. PMID: 12665469 Review.
-
Emerging Role of E2F Family in Cancer Stem Cells.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 12;11:723137. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.723137. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34476219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E2F Transcription Factors Control the Roller Coaster Ride of Cell Cycle Gene Expression.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1342:71-88. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2957-3_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26254918 Review.
Cited by
-
Divide or Commit - Revisiting the Role of Cell Cycle Regulators in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Apr 24;7:55. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00055. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31069222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Attenuates High Glucose-Induced Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury by Activating the E2F3 Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 28;2020:6173618. doi: 10.1155/2020/6173618. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32420356 Free PMC article.
-
MUC1-C Activates the BAF (mSWI/SNF) Complex in Prostate Cancer Stem Cells.Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 15;81(4):1111-1122. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2588. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33323379 Free PMC article.
-
Core signaling pathways in ovarian cancer stem cell revealed by integrative analysis of multi-marker genomics data.PLoS One. 2018 May 3;13(5):e0196351. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196351. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29723215 Free PMC article.
-
EIF5A2 enhances stemness of epithelial ovarian cancer cells via a E2F1/KLF4 axis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Mar 16;12(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02256-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33726845 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

