Prediction of high-risk types of human papillomaviruses using statistical model of protein "sequence space"
- PMID: 25972913
- PMCID: PMC4418008
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/756345
Prediction of high-risk types of human papillomaviruses using statistical model of protein "sequence space"
Abstract
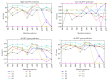
Discrimination of high-risk types of human papillomaviruses plays an important role in the diagnosis and remedy of cervical cancer. Recently, several computational methods have been proposed based on protein sequence-based and structure-based information, but the information of their related proteins has not been used until now. In this paper, we proposed using protein "sequence space" to explore this information and used it to predict high-risk types of HPVs. The proposed method was tested on 68 samples with known HPV types and 4 samples without HPV types and further compared with the available approaches. The results show that the proposed method achieved the best performance among all the evaluated methods with accuracy 95.59% and F1-score 90.91%, which indicates that protein "sequence space" could potentially be used to improve prediction of high-risk types of HPVs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of High-Risk Types of Human Papillomaviruses Using Reduced Amino Acid Modes.Comput Math Methods Med. 2020 Jun 18;2020:5325304. doi: 10.1155/2020/5325304. eCollection 2020. Comput Math Methods Med. 2020. PMID: 32655680 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances on Prediction of Human Papillomaviruses Risk Types.Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(3):236-243. doi: 10.2174/1389200220666190118110012. Curr Drug Metab. 2019. PMID: 30657038 Review.
-
Biology and pathological associations of the human papillomaviruses: a review.Malays J Pathol. 1998 Jun;20(1):1-10. Malays J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 10879257 Review.
-
Evaluation of human papillomavirus-consensus primers for HPV detection by the polymerase chain reaction.Mol Cell Probes. 1999 Feb;13(1):9-21. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1998.0203. Mol Cell Probes. 1999. PMID: 10024428
-
Protein intrinsic disorder and human papillomaviruses: increased amount of disorder in E6 and E7 oncoproteins from high risk HPVs.J Proteome Res. 2006 Aug;5(8):1829-42. doi: 10.1021/pr0602388. J Proteome Res. 2006. PMID: 16889404
Cited by
-
MicroRNA let-7 and viral infections: focus on mechanisms of action.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Feb 14;27(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00317-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35164678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyploid Giant Cancer Cells, a Hallmark of Oncoviruses and a New Therapeutic Challenge.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 14;10:567116. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.567116. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33154944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mathematical Modeling and Computational Prediction of High-Risk Types of Human Papillomaviruses.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jul 21;2022:1515810. doi: 10.1155/2022/1515810. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35912141 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

